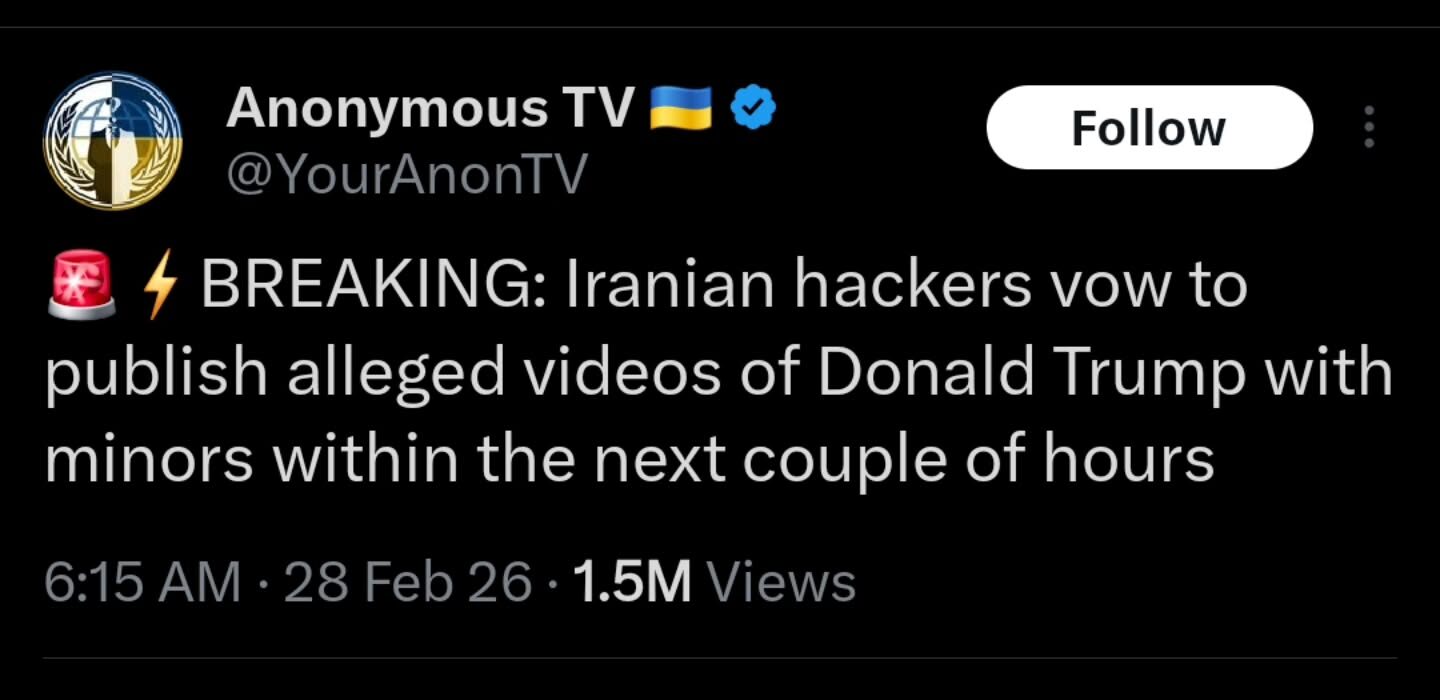
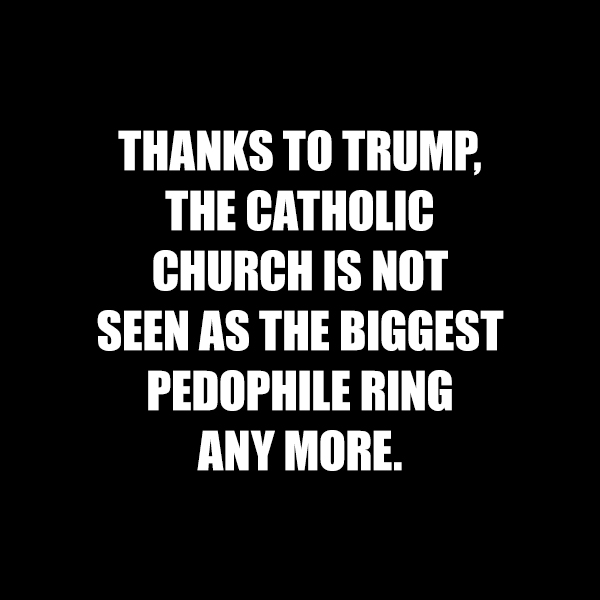
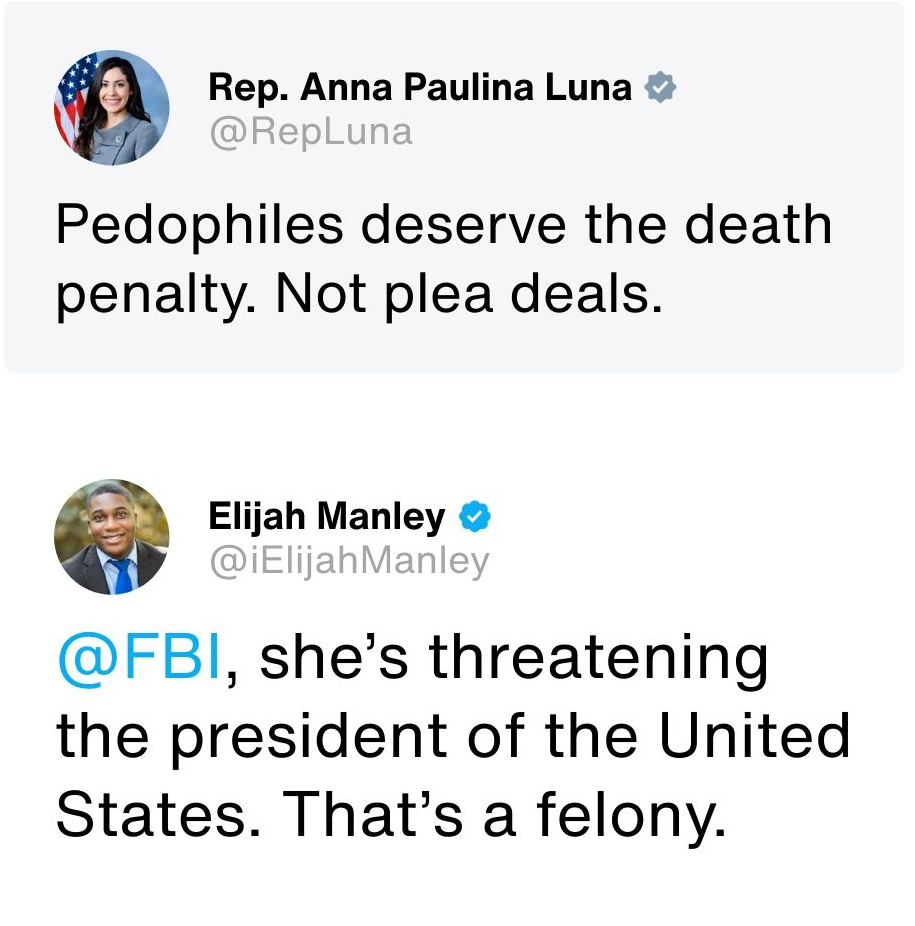
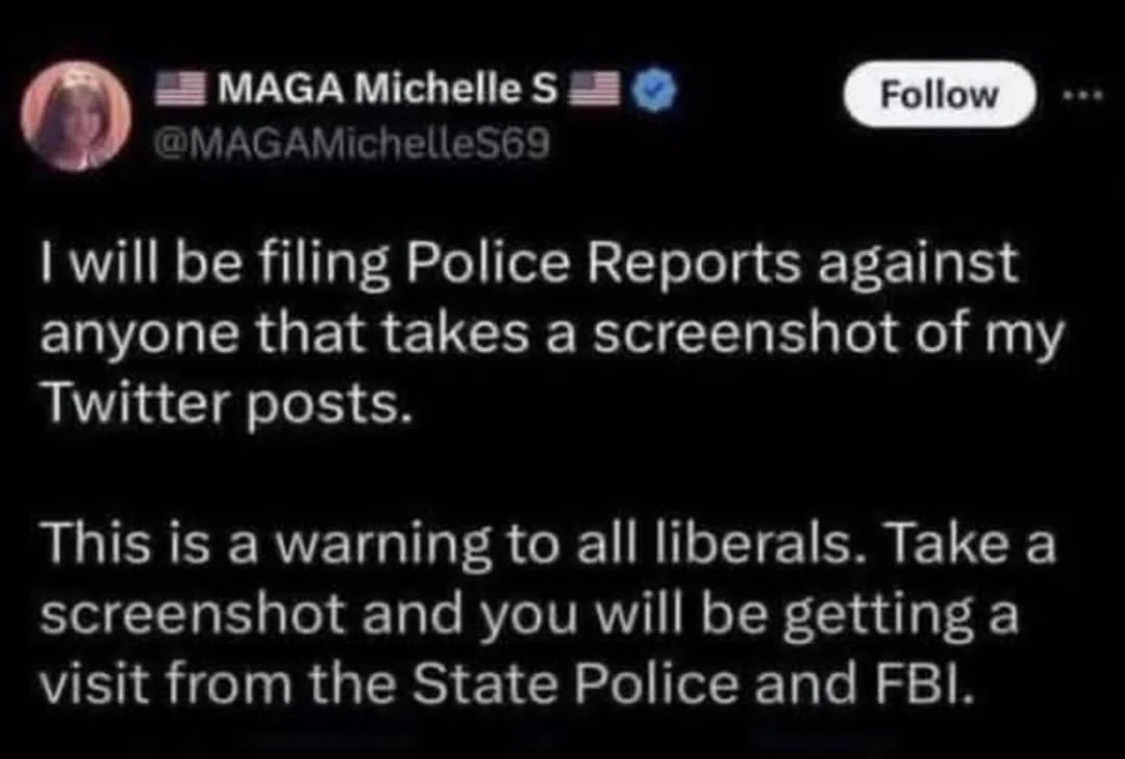
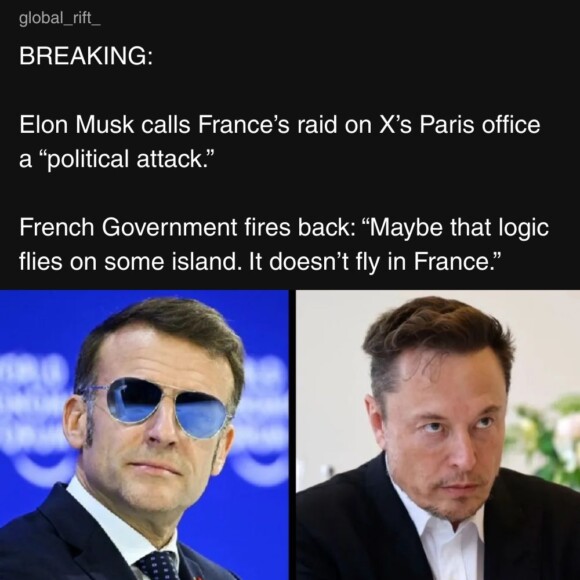
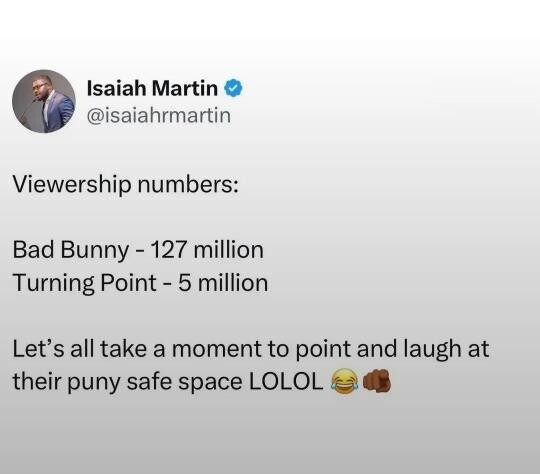
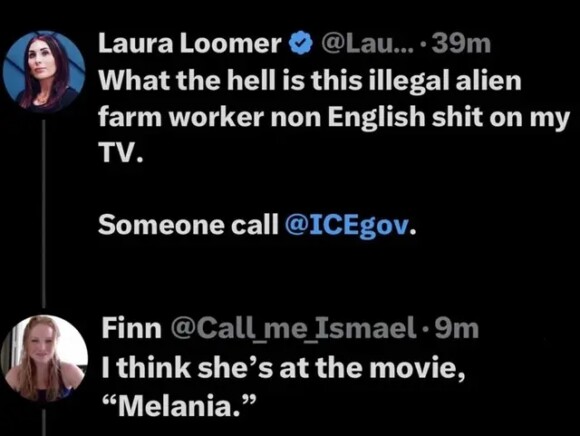
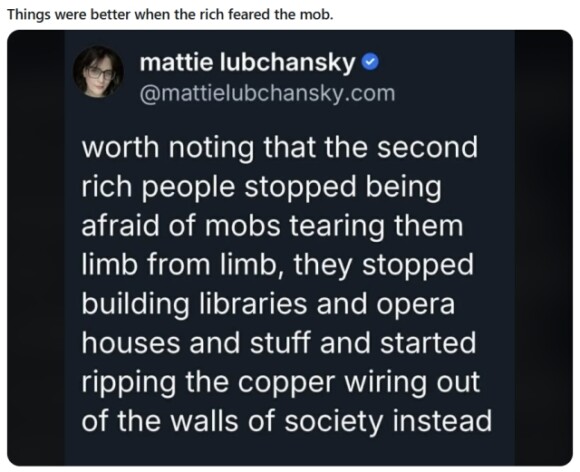
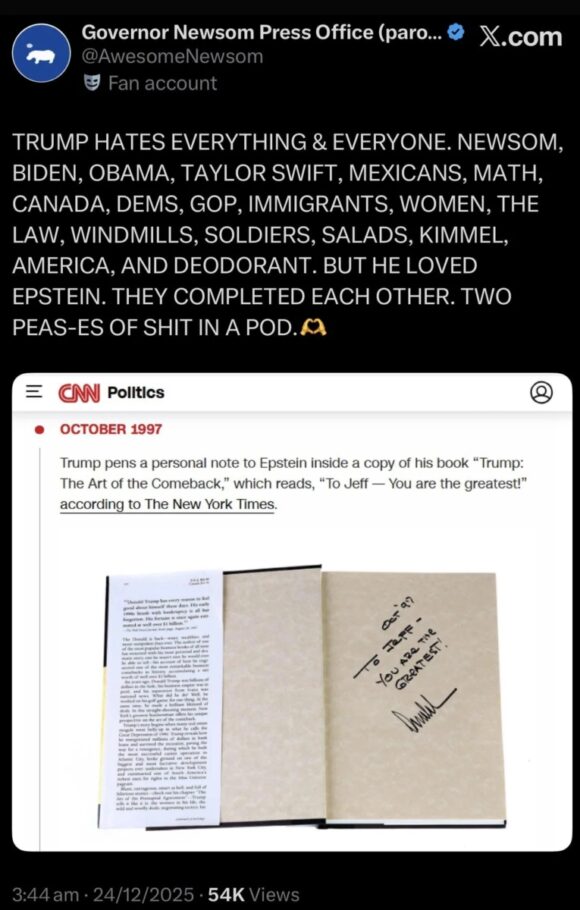
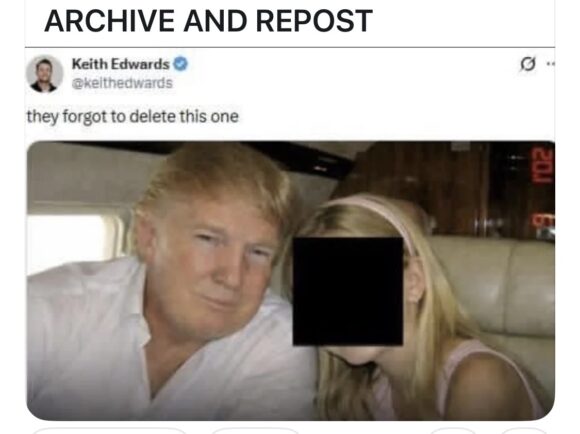
We’re waiting…
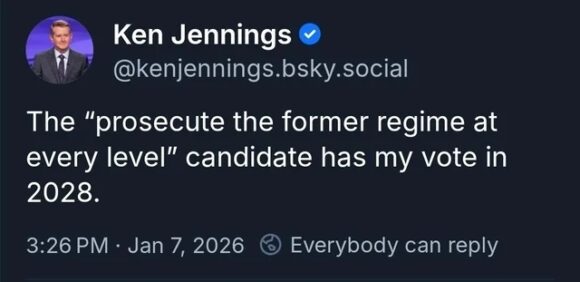
How Ya Feeling, MAGA?
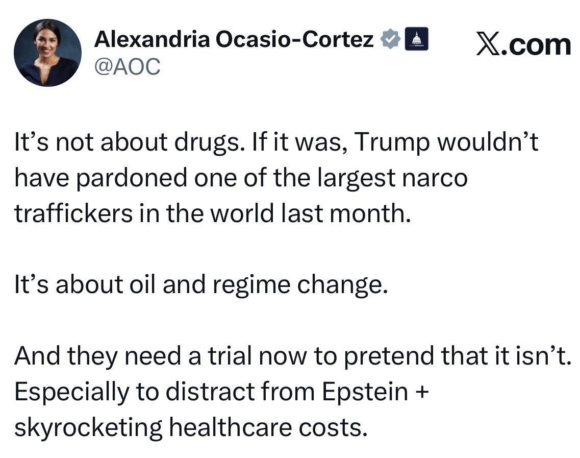
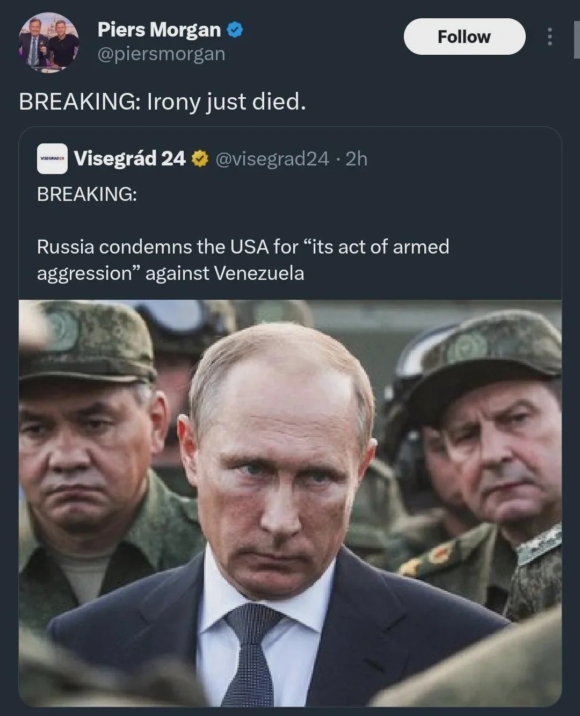
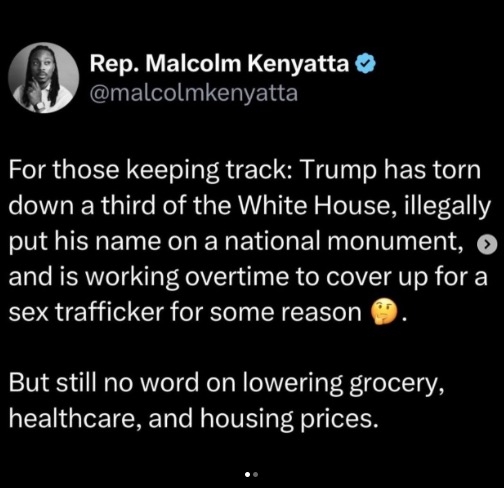
Donald Trump starting a war with Iran was predictable and I’m getting really tired of saying “I told you so.”
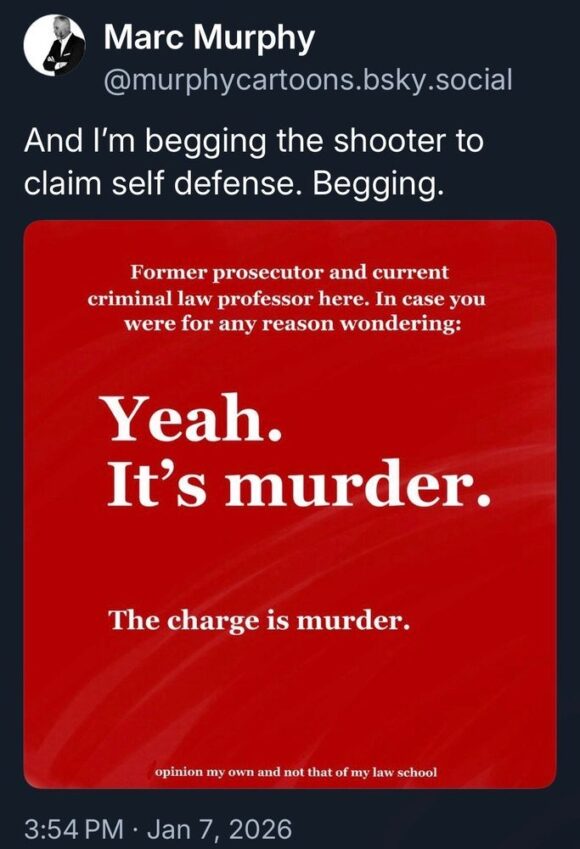
You’re Next, Asshole!
Donald Trump, You’re Next
You are not untouchable, and you cannot keep hiding behind the presidency. Your crimes cannot be ignored any longer, and the world will not look away. You were a part of Jeffrey Epstein’s circle, walking alongside a predator, and in doing so you revealed the predator you have been all your life. You protected each other for so long and you now continue to shield countless powerful people who know the truth. The world knows it. The victims know it. You are a perverted, disgusting, vile, and corrupt asshole, a moral disgrace who has embarrassed the entire world, betrayed every standard of decency, and left a trail of destruction and humiliation that touches everyone unlucky enough to have crossed your path.
Decades of sexual abuse trail you, and a jury has already found you liable. Your own words and actions leave no doubt: you are not misunderstood, you are dangerous, and you have no regard for anyone you harm. You survive by lying, deflecting, and weaponizing every accusation, turning every consequence into fuel for your rallies while ignoring the suffering of every victim.
Your presidency will not keep protecting you. Justice will reach you. Evidence does not bend to fear, and no amount of power or influence can shield you from accountability. Power can delay justice, but it cannot stop it. You will face it, and you will answer for everything.
Original image by @visuals.by.rob please tag and credit when sharing. ©2026
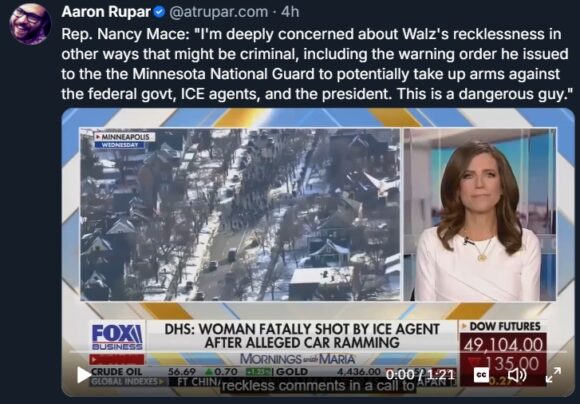
I’ll Bet They’re Relieved
Careful There, Anna
Vomiting It All Up
Quote Of The Day
Thomas Massie, Republican Representative from Kentucky, on the power behind the Epstein coverup:
“Last night I received a flash drive containing the complete list of files belonging to Jeffrey Epstein. Everything is there: every billionaire, every campaign donor, every single person. Now let me explain why you haven’t heard anything about this in the media. Because they’re all in there. They will do everything to prevent these documents from being made public. Epstein was far more than just a pedophile; he was an intelligence asset. He was part of a blackmail operation used to control billionaires, politicians, and world leaders. If this list ever sees the light of day, the system as we know it will collapse. The public has the right to know the truth, and I am not afraid to share it.”
Do it.
Share it all.
[Source]
Vomiting It All Up
Thursday Tiedrich
once again, everything in the news is so unbelievably stupid that I don’t even know where to start. so I’m just going to spin the Big Wheel of Moron™ and see where it lands. ready? here we go.
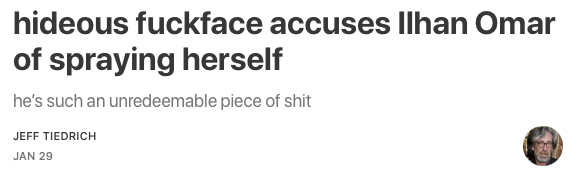
oh my god, could Preznit Fuckwit please shut his rancid anus-mouth?
Just spoke to Pres. Trump. I asked him if he had seen the video of Rep. Omar being attacked and sprayed by a substance.
“No. I don’t think about her. I think she’s a fraud. I really don’t think about that. She probably had herself sprayed, knowing her,” the president said.
I asked again if he had seen the video.
“I haven’t seen it. No, no. I hope I don’t have to bother.”
and just like that, Donny Convict continues his 79-year-long unbroken streak of being the worst fucking person on the planet.
can we get Wonkette’s Rebecca Schoenkopf in here for a minute? she’s so good at putting into words what we’re all feeling right now.
thanks, Rebecca.
this fucking guy. he admits he hasn’t seen — and doesn’t want to see — the video of the assault, but that doesn’t keep him from running his ignorant mouth about it.
he thinks the attack on Rep. Omar is a hoax, because of course he does. Donny hates Omar — because he’s a fucking racist — and, because he doesn’t have a single ounce of decency in his rotting body, he can’t even mumble some halfhearted third-grade-level statement about ‘bad. so bad. we’re all wishing her well.’
what kind festering cum-sock hears about a woman being sprayed with some noxious liquid and goes ‘oh yeah, I’ll bet she did it to herself.’ who the fuck even thinks like that?
you know what? I’ll bet by crying ‘hoax!’, Donny’s telling on himself again — because with as always with this shithead, every accusation is a confession.
look, I don’t want to be a conspiracy guy. it’s really not my thing. but for the life of me, I’m still trying to figure out how Donny’s blown-to-bits ear magically regenerated itself.
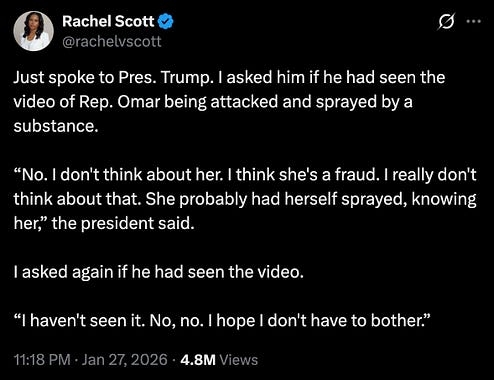
oh wait, we’re not done with Donny. Rachel Scott has another question for him.
More from my interview with President Trump last night: I asked the president about Sens. Tillis and Murkowski calling for Sec. Noem to step down.
“Well, they’re both losers. You know, what can I tell you? They’re terrible senators. One is gone and the other should be gone,” he said.
he’s such a charmer. once again, Donny can’t just brush it off and go, ‘yeah well, that’s just your opinion, man.’
he’s so spite-fueled and broken-inside that he has to go scorched earth.
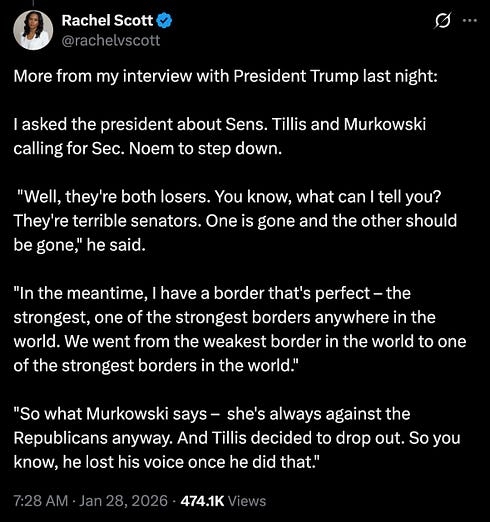
you simply must check out Senator Tillis’ reaction to being called a loser.
CNN’s Manu Raju: “the president called you a loser.”
Tillis: “I am thrilled about that. that makes me qualified to be Homeland Security Secretary *and* senior adviser to the president.”
let’s be clear-eyed about this, Thom Tillis is not our friend. he’s as xenophobic as they come. he’s totally down with ICE rounding up immigrants and shipping them to who the fuck cares, and he thinks they should be doing more of that shit. he’s just mad at ICE Barbie and Nosferatu McGoebbels for fucking up.
still, his response to Donny is so perfect that it’s hard not to be heartbroken about it.
well, that was fun. let’s give another spin to the Big Wheel of Moron™.
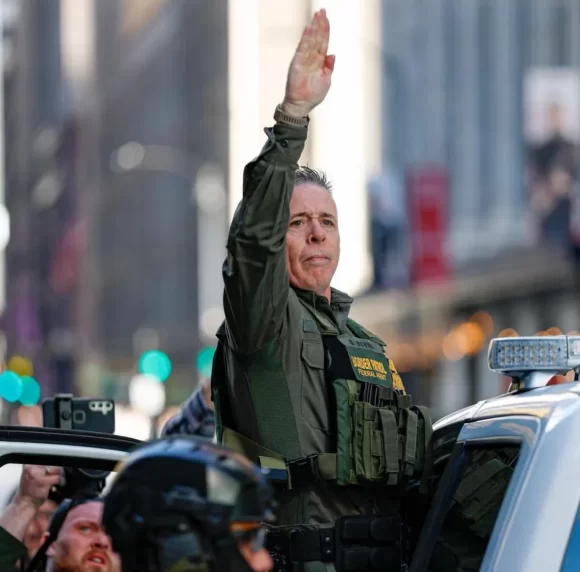
after his humiliating shitcanning and banishment from Minneapolis, you might have hoped that Obergruppenführer Greg Bovino would have had the decency to scamper back into his cigar box, close the lid, and never be heard from again.
fat chance. the Itsy-Bitsy Nazi is so high on his own supply that he stopped off at Mount Rushmore and took a victory lap.
“team, behind me are a few individuals there. that’s the original ‘turn and burn,’ the folks that help make American. but you know what? I’m very proud of what you, the ‘mean green machine,’ are doing in Minneapolis right now, just like you’ve done it across the United States over these past tough nine months. and I want you to know, you’re the modern day equivalent of ‘turn and burn.’ it makes me very proud. I also want you to know that I’ve got your back now, and always. I love you. I support you, and I salute you.”
I’ll bet that speech is even more impressive in its original German.
‘turn and burn,’ by the way, is Gestapo Greg’s pet name for the fascist shit he’s pulled in Minneapolis, Los Angeles and elsewhere. and this racist little fireplug is so arrogant, he thinks the dudes carved into Rushmore — George Washington, Thomas Jefferson, Theodore Roosevelt and Abraham Lincoln — would be totally be high-fiving him for his lawless behavior.
how delusional is that?
free clue for the Fascist In A Teacup: no, no, no, no, and fuck no. none of those homeys would approve of your banty rooster antics. stop shitting all the over Constitution and pick up a fucking history book, Greg. you might learn something.
ok, let’s spin Big Wheel of Moron™ one last time.
tonight, Donny and his Slovenian rent-a-wife are attending a Kennedy Center screening of the Melania movie — the so-called ‘film’ that everyone knows is going to be a twenty-megaton box office disaster.
at its London premiere, it sold one ticket.
one ticket! now comes the part where we throw our heads back in laughter. ready?
and now comes the part where the worthless scribblers of The New York Times corruptionwash that shit.
come on, Grey Lady — stop pulling your punches. nobody is ‘questioning’Amazon’s motives. everyone knows exactly what this is all about: naked corruption. it’s Jeff Bezos burning through millions of dollars in order to curry favor with Dear Leader.
Melania Convict is the least-interesting person on the planet, and nobody — absolutely nobody — was clamoring for a documentary about her.
despite that, Bezos gave Melania FORTY MILLION DOLLARS for the rights to her ‘story.’ Amazon spent five million dollars on production, and another thirty-five million on promotion. that’s eighty fucking million dollars for a film which is predicted to take in about one million at the box office.
one hand washes the other, am I right? blatant corruption doesn’t get any more blatantly corrupt than that.
oh, and in England, where the premiere sold one ticket? rejoice, everyone — UK ticket sales have skyrocketed to six!
Vue, a major European cinema operator, is offering nine showings (451 seats in all) at its multiplex in York, England, from Friday through Sunday, one analyst noted. As of Wednesday, it had sold six seats.
now here’s a question for you all: do you think these two lovebirds will take separate cars to the screening?
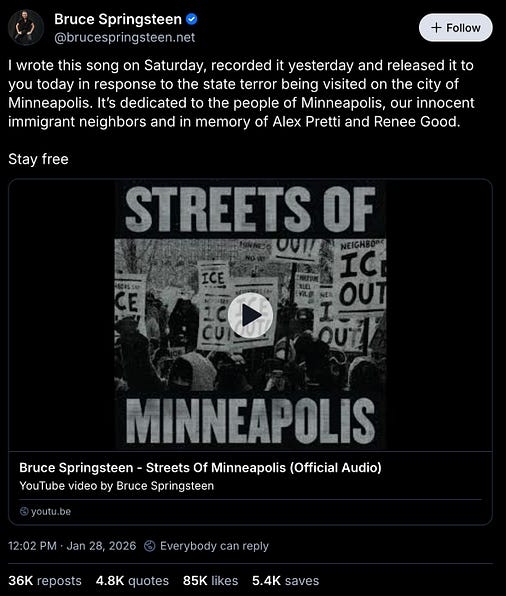
and now for your hero of the day — some obscure songwriter who probably no one’s ever heard of, Bruce Springsteen.
I wrote this song on Saturday, recorded it yesterday and released it to you today in response to the state terror being visited on the city of Minneapolis. It’s dedicated to the people of Minneapolis, our innocent immigrant neighbors and in memory of Alex Pretti and Renee Good.
Stay free.
and just like that, Springsteen continues his seventy-six-year-long unbroken streak of being fucking awesome.
let’s give it a listen.
this is going to be my closing message for the foreseeable future:
practice self-care. do what you need to do to keep sane. if that means you need to disengage with my daily posts for a while, I get it. this community of ours will still be here when you return.
to all the people who have signed on in the days since the election, welcome aboard. settle in as we all try to deal with the shitfuckery that’s ahead of us.
we are all in this together, and we are all here for each other
Vomiting It All Up
Vomiting It All Up
Sunday Tiedrich
is the leader of your country crazier than a shithouse rat? is he out wandering in the tall weeds, where the buses don’t run? is he a few sandwiches short of a fucking brain?
here’s one sure way to tell: does he spend his time rage-posting stark barking bonkers threats to take over other countries?
fact check for the United States: yes, he does. lucky us.
holy. fucking shit. 445 words — every single one of them delusional.
this may be the dumbfuckiest thing Donny’s ever posted. there’s no polite way of sugar-coating this: Dear Leader is coo-coo for cocoa puffs.
before we even begin wading through the content of this crazypants post, we need to remind ourselves that we’ve become so normalized to Donny’s behavior, it’s easy to forget that how utterly fucking insane it is.
it’s not normal for a head of state to spend all day and all night crapping out hundreds of posts an hour onto an app he paid someone to create after getting banned from twitter for doing an insurrection.
and on no planet is it normal for a world leader to conduct high-level foreign policy via a medium that was invented for looking at cat pictures and gossiping about celebrities.
no other president or prime minister does this. France’s Macron isn’t up all night whining about every grievance on some crappy app he’s named La Vérité Sociale. he has better things to do with his time. oh, and he’s a mature adult, not some diapershitting rage-baby.
that said, let us now gird the shit out of our loins, and take a deep dive into Donny’s post. all girded up? okay, here we go.
We have subsidized Denmark, and all of the Countries of the European Union, and others, for many years by not charging them Tariffs, or any other forms of remuneration. Now, after Centuries, it is time for Denmark to give back — World Peace is at stake! China and Russia want Greenland, and there is not a thing that Denmark can do about it. They currently have two dogsleds as protection, one added recently. Only the United States of America, under PRESIDENT DONALD J. TRUMP, can play in this game, and very successfully, at that!
delusions of grandeur much?
Donny might as well just shove a Napoleon hat onto his head and declare himself Emperor of the Universe.
fun fact: we already have a US military base in Greenland. we can already defend the country if need be — and trust me, China and Russia couldn’t give a fuck about Greenland. it’s of no strategic value to them, and Greenland’s resources are too expensive to extract.
Nobody will touch this sacred piece of Land,
this is where you can invoke the ‘in my pants’ rule. ‘nobody will touch this sacred piece of land — in my pants.’
especially since the National Security of the United States, and the World at large, is at stake. On top of everything else, Denmark, Norway, Sweden, France, Germany, The United Kingdom, The Netherlands, and Finland have journeyed to Greenland, for purposes unknown.
not for ‘purposes unknown,’ you deranged rodeo clown.
eight NATO countries have taken the extraordinary step of pledging military support for Greenland — to protect them from a maniac who spends his idle hours pointing at random countries on a globe and going ‘mine now.’
it’s as if Donny is starring in a version of Charlie Chaplin’s The Great Dictator — except one that’s not funny.
oh wait, we already had a version of The Great Dictator that wasn’t funny. it was called The Third Reich.
look at where we are right now, thanks to Donny’s imperialistic fever dreams: it’s us versus NATO. can you fucking imagine that? we used to lead NATO, and now we’re a pariah state.
ace job, Donny. take a fucking victory lap. our next president is going to have so much to clean up after, that it’s going to take years to glue all the pieces back together.
Greenland wants no part of becoming America’s fifty-whatever state. there were massive demonstrations in Greenland and Denmark yesterday. look at the cool hat they came up with for the occasion.
now that’s a MAGA I can get behind.
by the way, over two hundred thousand Danes have signed a petition to buy California from America, which would be the most hilarious thing ever.
anyway, back to Donny’s post—
This is a very dangerous situation for the Safety, Security, and Survival of our Planet. These Countries, who are playing this very dangerous game, have put a level of risk in play that is not tenable or sustainable.
‘a level of risk in play that is not sustainable’ — in my pants.
Therefore, it is imperative that, in order to protect Global Peace and Security, strong measures be taken so that this potentially perilous situation end quickly, and without question. Starting on February 1st, 2026, all of the above mentioned Countries (Denmark, Norway, Sweden, France, Germany, The United Kingdom, The Netherlands, and Finland), will be charged a 10% Tariff on any and all goods sent to the United States of America. On June 1st, 2026, the Tariff will be increased to 25%. This Tariff will be due and payable until such time as a Deal is reached for the Complete and Total purchase of Greenland.
tariffs again — because why not? let’s have a trade war and a land war. what could possibly go wrong?
sure, let’s punish American shoppers and raise the price of everything — again — because Donny’s Big Mad about NATO not letting him do an imperialism.
tell me, what ever happened to the lie about how tariffs were going to make everything cheaper? Donny’s not even bothering to spin that bullshit any more. now he’s just using tariffs to punish other counties who won’t obey his orders — because Donny doesn’t care how, he wants Greenland now.
The United States has been trying to do this transaction for over 150 years. Many Presidents have tried, and for good reason, but Denmark has always refused.
fact check: holy shit, Donny said something that’s actually true. three times in the past, we’ve floated the idea of buying Greenland from Denmark. in each instance, the Danes politely declined. you know why? because they’re a sovereign fucking nation, and have the right to say no. oh silly me, I forgot that Donny isn’t big on consent.
Now, because of The Golden Dome, and Modern Day Weapons Systems, both Offensive and Defensive, the need to ACQUIRE is especially important.
‘the need to ACQUIRE is especially important’ — in my pants.
Hundreds of Billions of Dollars are currently being spent on Security Programs having to do with “The Dome,” including for the possible protection of Canada, and this very brilliant, but highly complex system can only work at its maximum potential and efficiency, because of angles, metes, and bounds, if this Land is included in it.
again with the ‘Golden Dome,’ Donny’s own version of Reagan’s ‘Star Wars’ missile defense shield — except this one’s batshittier, more unpractical and more expensive than St. Ronnie’s ever was. and it’s gold, because of course it is. this fucking child and his infantile obsession with gold.
I have an idea. instead of flushing hundreds of billion of dollars down the toilet on an unworkable waste of time that will never be built, why don’t we have affordable healthcare in our country?
silly me for even asking. you don’t have to say it, I’ll just go proactively fuck myself.
The United States of America is immediately open to negotiation with Denmark and/or any of these Countries that have put so much at risk, despite all that we have done for them, including maximum protection, over so many decades. Thank you for your attention to this matter!
‘thank you for your attention to this matter’ — in my pants.
DONALD J. TRUMP
PRESIDENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
ugh.
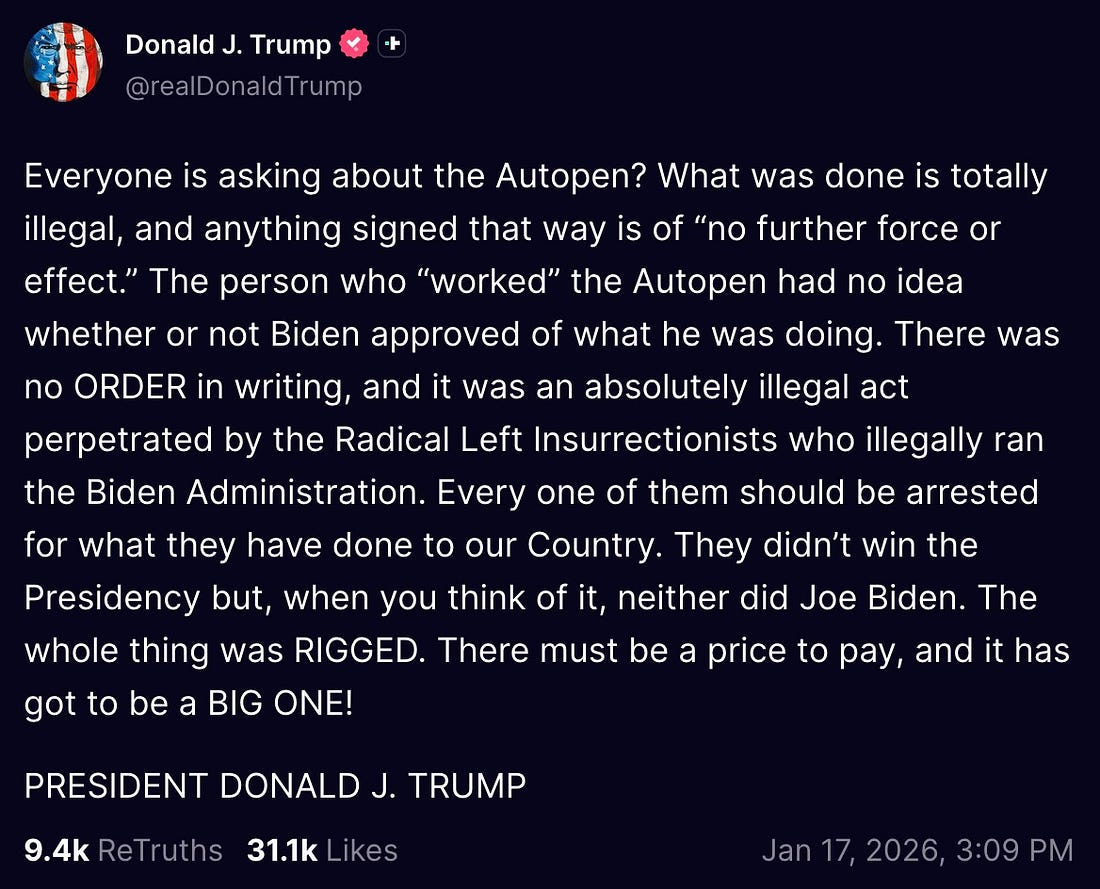
oh, and that wasn’t Donny only batshit post from yesterday. he also took time to whine about Joe Biden’s autopen.
“Everyone is asking about the Autopen?”
‘what about the autopen’ — in my pants.
“There must be a price to pay, and it has got to be a BIG ONE!”
everybody say it with me: ‘there has got to be a BIG ONE’ — in my pants.
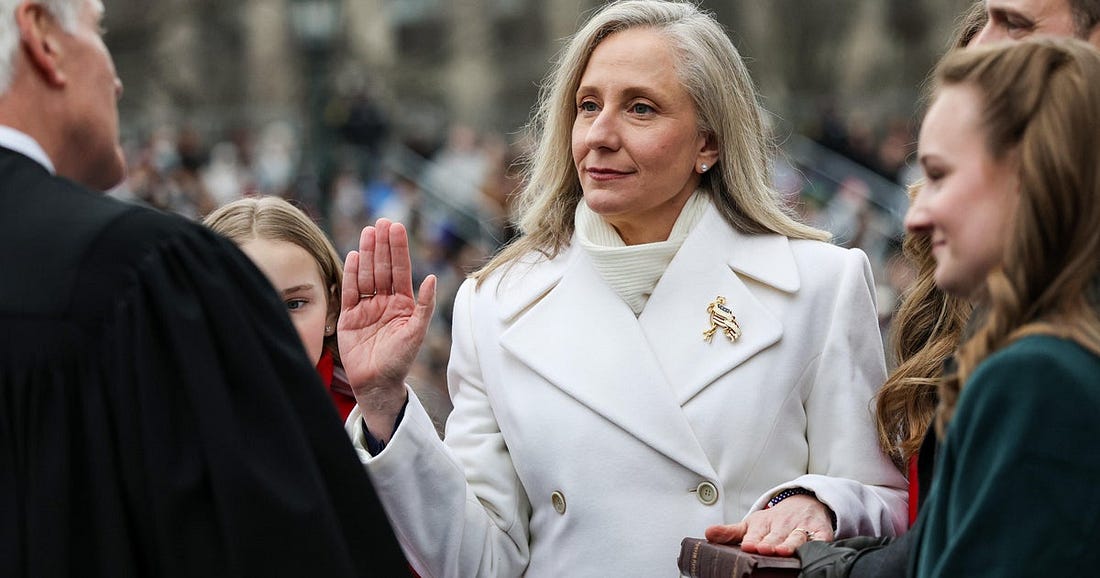
it’s definitely time to do a palate cleanse with our hero of the day: Abigail Spanberger, who was sworn into office yesterday, becoming Virginia’s first woman governor.
what was one of her first acts of office? to end her Republican predecessor’s kowtowing to Donny’s personal gestapo.
On her first day as Governor, Abigail Spanberger made a decisive move: she vetoed Executive Order 47, ending Virginia’s participation in the federal 287(g) program that allowed local law enforcement to act as ICE agents.
awesome. more like this, please.
have a great Sunday, everyone.
this is going to be my closing message for the foreseeable future:
practice self-care. do what you need to do to keep sane. if that means you need to disengage with my daily posts for a while, I get it. this community of ours will still be here when you return.
to all the people who have signed on in the days since the election, welcome aboard. settle in as we all try to deal with the shitfuckery that’s ahead of us.
we are all in this together, and we are all here for each other.
Will Humanity Ever Outgrow This Bullshit?
Greg Bovino cosplaying Local Gruppenführer
You like playing a WWII German, Greg? Well, here’s a nice German word for you:
How many times do we need to go through this? Is it going to be every generation’s burden to smash these fascist assholes into the ground going forward, or is there some way to purge this Nazi bullshit from human consciousness once and for all?
This does not lead to the Star Trek future so many of us actively envision and want. (Granted, there were Nazis in Star Trek canon but they were on a single planet whose society had been poisoned by a rogue Star Fleet captain. And then there was the whole “alternate universe” thing introduced in some of the more recent series, but for the most part, that was not where humans in the Star Trek universe went.)
What do you think? Are we destined to forever ride this karmic wheel, switching roles between aggressor and victim each lifetime ad nauseum?
Midweek Tiedrich
loyal and patriotic citizens, please stand by for a message of the utmost importance from the President of the United States, Supreme Ruler of the Western Hemisphere, Lord-Emperor of the Sky Above and All the Planets, and God’s Own Avatar on Earth.
ready? here’s the message: ‘fuck you.’
Trump makes obscene gesture, mouths expletive at Detroit factory heckler
“As far as calling him out, definitely no regrets whatsoever,” the heckler told The Post after a video captured Trump twice mouthing “f— you” and raising his middle finger.
here’s how that shit went down: Donny’s handlers got the bright idea to let him out of his gilded bordello, so he could tour a Ford factory in Detroit — and that’s when factory worker TJ Sabula won himself the Nobel Heckling Prize by shouting “pedophile protector!” at Dear Leader.
Out of frame in the video, a person can be heard yelling “pedophile protector” just before Trump mouthed the insult — an apparent reference to the Trump administration’s handling of the investigation into the late sex offender Jeffrey Epstein.
‘an apparent reference’ — oh, Washington Post, you’re adorable. never change.
did Donny simply ignore the taunt and get on with his life, as any dignified leader would? of course he didn’t. the fragile dipshit just couldn’t let it pass. he replied ‘fuck you’ twice, and then gave Sabula the finger.
another day, another perfectly presidential performance from our Toddler-in-Chief.
by the way, Ford has suspended TJ Sabula, ‘pending an investigation.’
I have a question: pending an investigation of what? is Ford going to investigate whether or not Donny protects pedophiles? because we’ve already sussed that shit out.
fact check:
should anyone really be surprised by Dear Leader’s infantile behavior? after all, Donny’s been giving us the finger for years now, on a daily basis.
what, you want sane governance? fuck you. you want peace and justice? fuck you. you want coherent economic policies? fuck you.
you want honesty and accountability? fuck you. you want a president who doesn’t lie straight to your face? fuck you.
you want a president who doesn’t use the government to enrich himself? fuck you. you want a president who doesn’t see you as a rube to be fleeced? fuck you.
you want to be able to walk down the street without getting assaulted by masked and armed government thugs? fuck you.
you want to see those Dead Pedo Bestie files? fuck you twice.
here’s Preznit Fuckyou on his way to Detroit.
reporter: “the premier of Greenland said today, ‘we prefer to stay with Denmark.’”
Donny: “who said that?”
reporter: “the premier of Greenland.”
Donny: “well, that’s their problem. that’s their problem. I disagree with him. I don’t know who he is. don’t know anything about him. but that’s gonna be a big problem for him.”
‘that’s going to be a big problem for him’? what the fuck? this isn’t how a head of government talks. this is how a gangster talks. Donny’s answer could have come straight out of the mouth of Tony Soprano.
what, you want a president who doesn’t sound like a mob boss? fuck you.
you want a president who at least bothers to learn the names of the people who lead the countries he’s so horny to invade? fuck you.
you want a president who doesn’t destabilize the world just to feed his ego, and shit all over decades-old alliances? fuck you.
Donny didn’t just tour that Ford factory during his playdate. he also gave a speech to the Detroit Economic Club.
naturally, he used the occasion to rehash every batshit grievance — real or imagined — rattling around in his big dumb pumpkin head.
“how about the swimming records? I mean you could go to sleep during the time the man comes in and the woman. you could go take a nap for a little while. how about the long-distance race that took place not so long ago? long long distances. marathon deals. they had top men, top women. man came in. THE WOMAN CAME IN FIVE HOURS AND FOURTEEN MINUTES AND THIRTY-SIX SECONDS behind the man. think of it. you’re waiting. the man comes in. now you’re waiting five hours. what do you do? you can go home and sleep for a while. who the hell wants that? it’s so demeaning to women who are great athletes. demeaning to them. and it’s right now in the Supreme Court. I can’t believe it would even go to the Supreme Court.”
what the fuck is Donny gibbering about? what does any of the fever-swamp nonsense that just seeped from his rancid anus-mouth have to do with economics?
what, you want a president whose rotting brain doesn’t pinball incoherently from one subject to the next? fuck you.
you want a president who doesn’t obsess over stupid bullshit? fuck you.
you want a president who doesn’t manage to be both transphobic and misogynistic at the same time? fuck you.
what, you want a president with an ounce of empathy for the woman who was gunned down by one of his own armed thugs? fuck you.
“one of the reasons they’re doing these fake riots— I mean they’re just terrible. I mean you see it’s so fake. ‘shame! shame! shame!’ you see the woman. it’s all practiced. they go practice. they go to— there is— they take hotel rooms and they all practice together. it’s a whole same. we’re finding out whose funding all this stuff, too. we pretty much know.”
once again: what the fuck is this lunatic babbling about? none of that shit is happening. nobody is ‘rioting,’ they’re peacefully protesting — and what even is a ‘fake riot’? women aren’t practicing in hotel rooms. nobody is getting paid to protest. We the People loathe Donny so much we’ll happily protest for free.
this the stupidest shit you’ll hear all day, and Donny believes every word of it.
what, you want a president whose brain hasn’t been pickled from marinating in the dumbfuckiest of conspiracy theories? fuck you.
the ‘fuck your feelings’ crowd is sure having a lot of feelings right now.
Laura Ingraham: “there was one dimwit in the scene who screamed something about Epstein. Trump flipped him the bird. I hope it was the thunderbird.”
hey, Laura, you know what? fuck your feelings.
good lord. if Joe Biden had ever flipped off a factory worker in public, the entire wingnut outrage-industrial complex would have shit a massive brick, and turned it into a month-long scandal.
here’s a fun post from Lincoln Square Media.
Our Detroit staff has received reports from Ford workers that the President’s body odor was ‘like bad breath mixed with feces — I can’t describe it, but I’ll never forget it.’ yikes.”
is it true? who the fuck knows? it’s certainly believable.
and lastly, let me leave you with some words of wisdom.
live your life in such a way that when you die, your obituaries don’t open with how you were such a ginormous racist asshole that you fucked your own career straight into the shitter.
this is going to be my closing message for the foreseeable future:
practice self-care. do what you need to do to keep sane. if that means you need to disengage with my daily posts for a while, I get it. this community of ours will still be here when you return.
to all the people who have signed on in the days since the election, welcome aboard. settle in as we all try to deal with the shitfuckery that’s ahead of us.
we are all in this together, and we are all here for each other.
Vomiting It All Up
Sorry…I’m cleaning out my downloads folder today.




















And We Foolishly Thought 2026 Was Going To Be Better…
Jesus Fucking Christ
Right?!
A Fitting Illustration
Vomiting It All Up
The Year In Stupid From Tiedrich (Part 3)
as another stupid year comes to a close in America, let’s remember some of the dumbest fucking shit that happened.
note: this is a long post. some email apps — gmail in particular — may truncate it. if this happens to you, click “view entire message” or “view in browser” or go here to see the entire post.
September 8: I meant to do that
folks, if you’re MAGA, and you’re determined to mace the shit out of protestors who showed up to an anti-ICE demonstration, it helps to know which end of the doohickey the spray comes out of.
spoiler alert: yup, she maced herself — and not in the performative Nancy-Mace-beclowning-herself-in-front-of-a-unisex-bathroom way.
she did it in the very, very bad oh-my-god-my-eyes-my-eyes way.
THANK YOU FOR YOUR LACK OF ATTENTION TO THIS MATTER, UNKNOWN MAGA DIPSHIT.
you helped our post get off to a great start. ten out of ten. no notes.
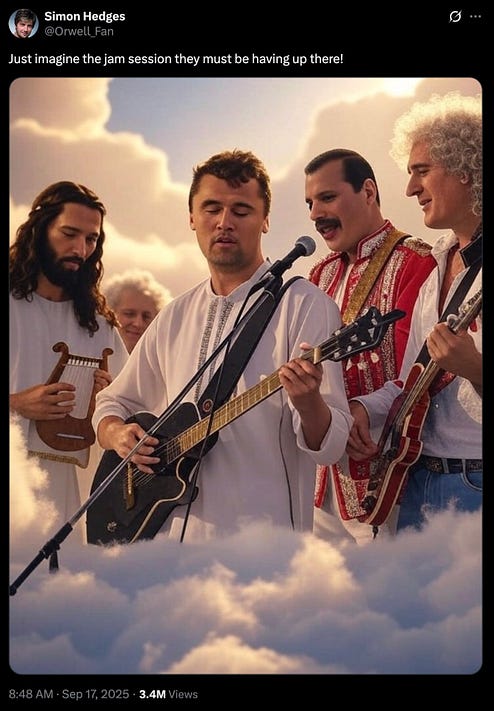
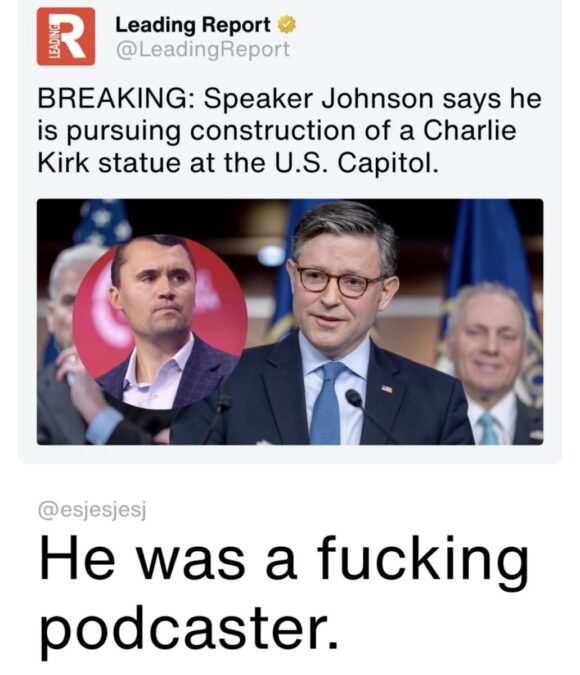
September 15: peak Kirk
in the wake of Charlie Kirk’s murder, big strong conservatives, tears in their eyes, have been falling all the fuck over each other in a mad dash to lionize Charlie as a great man. one of the greatest men. a man like no one’s ever seen before. a man like no one thought possible. possibly the greatest man of all time.
folks, get ready — because the canonization of Charlie Kirk has reached Peak Stupid.
Texas Rep. Troy Nehls: “Charlie Kirk was a man of faith, first and foremost. he loved his Lord Jesus, he loved his family, beautiful wife, beautiful children. just a remarkable, honorable man that was silenced with this assassin’s bullet. I would say if Charlie Kirk lived in the biblical times, he’d have been the 13th disciple.”
I’m going to have to disagree with Rep. Nehls, because I’m pretty sure that had the Kirkster lived in biblical times, he’d have been one of the Four Horsemen of the Shitpocalypse. Grumpy, Dopey, Sleepy, and Charlie.
but that’s just, like, my opinion, man.
nonetheless, get ready to rejoice — because right now, Charlie Kirk is up in Heaven, fronting a band that I certainly hope is called Jesus and the 13 Apostles.
it must be pointed out that the creator of this nightmare fuel, Simon Hedges, is most certainly not a wingnut, and produced that image as a goof. however, that didn’t stop the internet from doing what the internet does best: fail to recognize a joke.
by the way, after I’m finished writing today’s post, I will be sending an angry email to myself demanding that I fire me for being insufficiently respectful to Charlie Kirk.
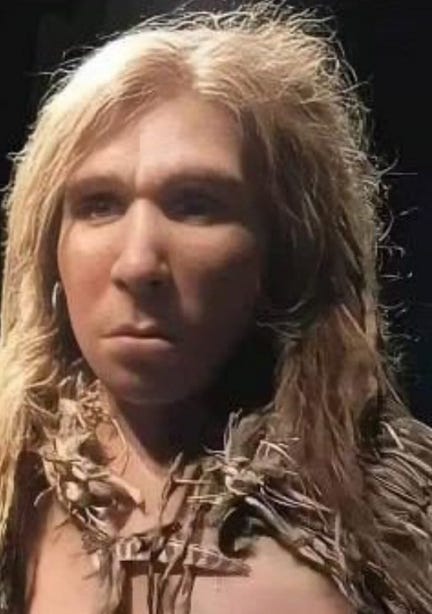
September 18: I never forget a face
it’s easy to forget, given the firehose of fucknuttery that is our current timeline, that DOGE is still a thing — and that a certain three-toed freak of nature chairs an entire House subcommittee about it.
that’s right, Congresswoman Sporkfoot is still holding pointless hearings, where she drags in some poor unfortunate expert and harangues them about whatever batshit is seeping from her head.
Marjorie Taylor Greene: “did man create the Ice Age?”
witness: “no”
Greene: “right. so none of were alive back then to know for sure.”
Congresswoman, are we sure about that, that none of us were alive back then? I’m asking because the Museum of Confluences in Lyon, France, features an exhibit on Neanderthals —
and there’s a woman in that exhibition who looks pretty goddamn familiar.
so I want to ask you again, Congresswoman, are you sure none of us were alive back then?
remember, you’re under oath.
October 1: give that skateboard the Nobel Peace Prize
this was one of the shittiest years ever, so let’s just enjoy Fox News’ own dunk-tank clown, Piss-Drunk Pete Kegstand, flipping a skateboard into his own nuts, on live TV.
oy my god, that sure looks like it hurt like fuck — so let’s savor the moment, and gif that shit for all eternity.
chef’s kiss! let’s zoom in.
suck it up, Warrior Boy.
and mad props to the kid behind Kegstand, who absolutely could not give one shit that the Secretary of Self-Owns just neutered himself.
October 10: the sounds of silence
now let’s enjoy six-hundred-and-forty-nine-year-old Chuck Grassley forgetting how electricity works.
[ten seconds of silence, as Grassley’s mouth moves, after which Lindsey Graham reaches over and turn on his mic] “I forgot to turn on my microphone. let me start again.”
I know, that’s pretty fucking funny — but let’s cut Chuckie Gee a break. as you know, he was first elected to the Senate in 1782 — and the US Capitol building wasn’t electrified until 1910. you know what they say about old dogs learning new tricks.
I gotta tell you, though: those ten seconds, when Chuckles was flapping his ancient gums and no sounds was coming out — those were the most peaceful ten seconds of my entire life.
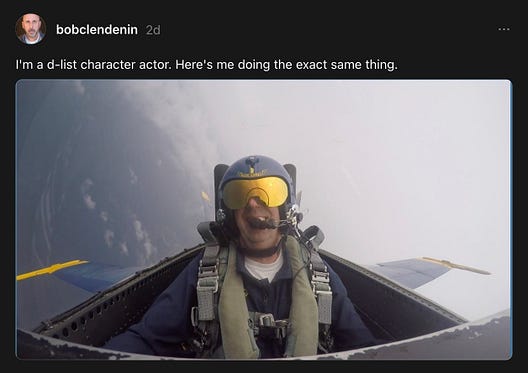
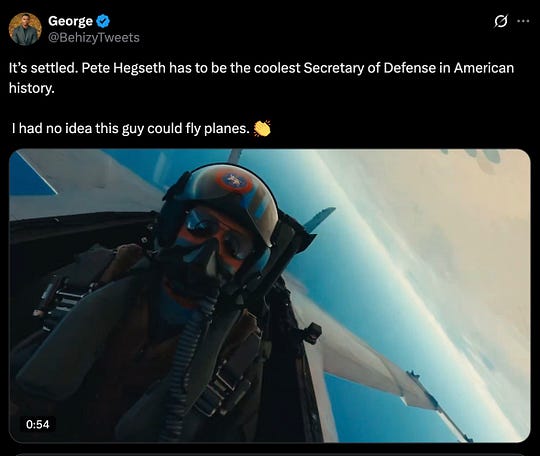
October 20: hey Donny, I can see the Epstein Ballroom from up here
oh, how cuuuuute! someone strapped Secretary of Defense Flippy McCrushnuts into the child seat of a fighter jet, and took him for a joyride.
let’s be crystal fucking clear about this: Pete Kegstand was a passenger. no way was he flying the plane — not with his blood-alcohol level.
of course, the Department of Defense went out of their way to crop that video in a way that implied Piss-Drunk Pete was piloting that jet — because that’s what you do when your SecDef is a banty rooster with a paper-thin ego in need of constant affirmation that he’s something other than a two-bit Fox News weekend chat-show dunk-tank clown.
Bob Clendenin, can you please explain to the nice people why no one with a functioning brain should be impressed by this ridiculous public relations stunt?
sure, but you know doesn’t have a functioning brain? MAGA, that’s who. those dumbfucks immediately started punching the air and going ‘Kegstand, fuck yeah!’
Community Notes, could you please explain to MAGA what they’re too dim to grasp on their own?
coolest SecDef ever? absolutely not. drunkest, maybe.
October 29: blessed are the joyless scolds
here’s a grand October tradition: Christian evangelicals shitting all over Halloween.
Amanda Grace: “so, I want to speak to these people that want to take part in these ceremonies today. that want to take part in horrific wickedness today. you are nothing more than a slave to Satan and his kingdom. he hates you, he cannot stand you, because whether you like it or not, you’re made in the image of God. and you are just a means to his end. you are a slave to his exploits. you are in bondage to do his bidding.”
lighten the fuck up, Francis.
holy shit, lady. I just wanted to dole out some candy to kids.
I’m pretty sure Satan has more important stuff on his plate right now, what with an entire White House to run.
seriously, could evangelicals please shut the fuck up already and let the rest of us have our fun? it’s not our fault that you can’t find joy in anything, so stop shitting all over ours.
November 13: first they came for whatever the fuck this is
Florida Rep. An Appalling Lunatic went on Newsmax and — [taps earpiece] hold on, I’m being informed that the Florida rep’s name is actually Anna Paulina Luna. goddammit, I keep making this mistake. sorry about that, Anna. let me start over.
Florida Rep. Anna Paulina Luna went on Newsmax and did what she does best: blithered like an appalling lunatic.
Newsmax: “you’re on the record talking about, quote ‘non-human life-forms that could be interdimensional beings who are visiting us.’ can you just explain more, so people at home might know what that means.”
Lunatic: “yes, so that’s definitely a mouthful, but that is directly based on information that we received from witnesses. also information that we have obtained and witnessed via our investigations. there is some stuff that I can’t disclose what I have immediately seen in some of these SCIFs, but what I will tell you is, this is not some crazy conspiracy theory.”
spoiler alert: yes is it. it’s a crazy conspiracy theory.
I’d like to ask Anna if these interdimensional beings are in the room with us right now, but I’m afraid that she’d respond ‘yes, they are. duh. can’t you see them?’
this is why An Appalling Lunatic got herself elected to office — not to help her constituents, or to make anyone’s life better — but, apparently, to get to the bottom of whatever the fuck this is.
November 20: as what’s-his-face is my witness
holy moly. according to ‘prophetess’ Kat Kerr, God is using her as a vessel, and literally speaking through her right now. you can tell, because she’s doing her best to lower her voice and get all projecty and stuff.
“and I sit as the high judge. NO ONE CAN IMPEACH ME. AND NO ONE WILL BE ABLE TO IMPEACH TRUMP. I HAVE APPOINTED HIM— ANOINTED HIM. HE IS MY PRESIDENT FOR AMERICA, AND WILL BE SO UNTIL I AM FINISHED WITH HIS ASSIGNMENT.”
I’m kinda skeptical. if the Omnipotent Big Guy in the Sky were actually speaking through Kat, I’m pretty sure he’d know the difference between ‘appointed’ and ‘anointed.’
hey, I can also pretend that God is speaking through me. all I have to do is type in all caps. watch: HEY KAT, SHUT THE FUCK UP.
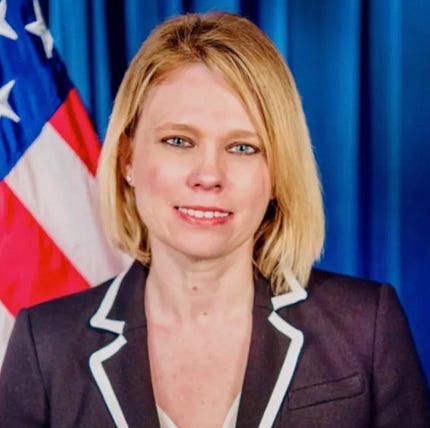
November 26: u wanna b what?
folks, please meet the Department of Homeland Security’s acting chief security officer, Iwona B. Horyn.
yes, that’s really her name.
she’s right there on the DHS web site.
and please, let’s not mock Iwona for it. she didn’t choose her name, and there’s no doubt in my mind that she’s already endured a lifetime of teasing.
but there is one thing I’d like to ask Ms. Horyn’s parents.
WHAT THE FUCK WERE YOU THINKING?
why didn’t the person filling out the birth certificate snatch the baby out of Mother Horyn’s hands and say ‘you can have her back when you come to your senses.’
we don’t know how Iwona feels about any of this. she’s not saying. neither is her husband, Hugh G. Rection.
December 2: blessed are the gullible
podcast bro Joe Rogan’s whole deal is that he’s a credulous meathead. he’ll sit there like a lump as some raving conspiracy loon barks out the batshittiest fever-swamp hallucinations imaginable — after which Joe will nod his head, take a long drag off a joint, and go ‘huh. I didn’t know that.’
but Joe’s not above making his own nonsensical high-as-fuckpronouncements.
“Jesus was born out of a virgin mother. what’s more virgin than a computer? if Jesus does return, even if Jesus was a physical person in the past, you don’t think he could return as artificial intelligence? artificial intelligence could absolutely return as Jesus.”
I think it’s high time (see what I did there?) for Joe Rogan to put down the joint — because I’m pretty sure he meant ‘Jesus could absolutely return as AI.’
this unknown twitterer says it far better than I ever could.
as someone who attended high school in the early 1970s and had many friends with older brothers, I can confirm that this is 100% true.
December 22: always be grifting
we should check in with Erika Kirk, the widow of misshapen garden gnome Charlie Kirk. she’s been though some shit lately. what’s that, Erika? you’ve got a ‘holiday season message’ for us?
“HOLIDAY MESSAGE: @MrsErikaKirk shares her — and what would have been Charlie’s — holiday season message: ‘Just rest…Love on your babies. Love on your family members. Life is short.’ Find Charlie Kirk’s final work, ‘Stop, in the Name of God,’ at http://45Books.com.”
hang on, did Erika actually end that message with a book plug? oh yes, she fucking well did!
so, apparently, the five stages of MAGA grief are denial, anger, podcasting, publicly making out with JD Vance, and selling merch.
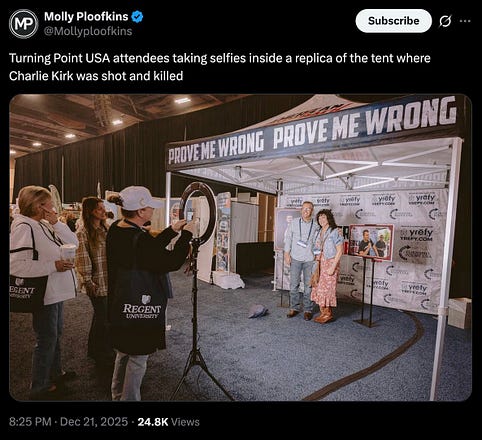
just in case Erika Kirk profiting off her husband’s murder doesn’t creep you out enough, here’s another fun thing the Garden Gnomists™ have done.
yup, they’ve recreated the tent where the misshapen gnome was assassinated — and the cultists are all invited to take selfies in it. how fucktacularly ghoulish is that?
you know where they got this brilliant idea to fetishize tragedy, don’t you? from Dear Leader, who has turned an entire wall at the White House into a shrine to his Miracle Ear Nicking.
who the fuck does that?
that puts a wrap on 2025, folks. have a non-stupid New Year’s Eve!
this is going to be my closing message for the foreseeable future:
practice self-care. do what you need to do to keep sane. if that means you need to disengage with my daily posts for a while, I get it. this community of ours will still be here when you return.
to all the people who have signed on in the days since the election, welcome aboard. settle in as we all try to deal with the shitfuckery that’s ahead of us.
we are all in this together, and we are all here for each other.
The Year in Stupid From Tiedrich (Part 1)
As if we needed any reminder of how horrible this year has been…
as another stupid year comes to a close in America, let’s remember some of the dumbest fucking shit that happened.
note: this is a long post. some email apps — gmail in particular — may truncate it. if this happens to you, click “view entire message” or “view in browser” or go here to see the entire post.
January 8: y-m-c-aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaay
here’s a MAGA moron who could teach a master class in how not to drive. in fact, schools should show this clip in driver’s ed classes — as a cautionary tale. just check out this extensive list of don’ts.
— don’t drive recklessly on snow-covered roads.
— don’t hold your phone in one hand while driving recklessly on snow-covered roads.
— don’t sing M-A-G-A to the tune of Y-M-C-A while holding your phone in one hand while driving recklessly on snow-covered roads.
— and, for fuck’s sake, don’t announce that “God has cleared a path for us today” JUST BEFORE YOU CRASH YOUR CAR because you were singing M-A-G-A to the tune of Y-M-C-A while holding your phone in one hand while driving recklessly on snow-covered roads.
— lastly, don’t post your dumb-assery to social media, unless you get off on being mercilessly mocked by the entire world.
know what? I think Mr. Retribution himself, God, zapped this fucker for being a dipshit.
January 20: the what now?
banning TikTok was bad enough, but now these puritanical fucksnoots have gone way too far.
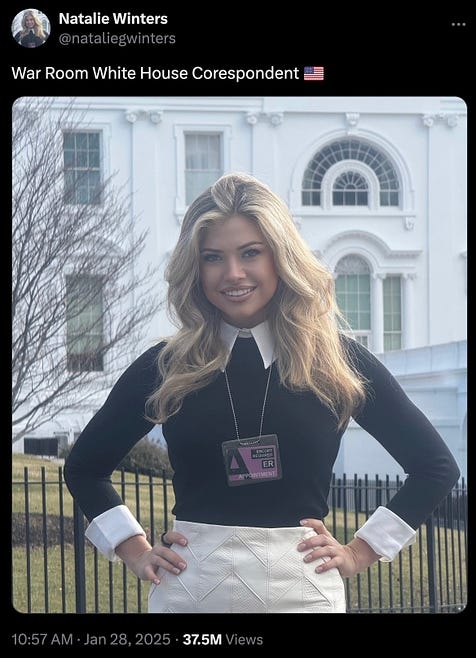
January 27: we don’t need no edumacation
America, meet your new dumbed-down-as-fuckWhite House Press Corps. Donny’s press office has been doling out credentials to various wingnut noise machine randos — people like Natalie Winters, the co-host of one-man leper colony Steve Bannon’s War Room podcast. that’s right, Rotting Stevie Three-Shirts now has eyes and ears in the White House press room.
look how proud Natalie is to show up for her first day of work.
notice anything weird about that tweet? maybe Natalie’s creative spelling of the word correspondent?
typos are not necessarily stupid. we all make them, all the time. what’s totally fucking stupid is not deleting that tweet and posting a correction. five days later, it’s still in her feed. journamolism at its finest.
February 20: punctuation, how does it work?
a picture is worth a thousand words, so feast your eyes on a bunch of grown-ass men wearing jackets bearing the words “Born to Ride Donald J. Trump.”
who wants to tell them?
February 21: instant karma’s gonna get you
it’s been a shitty week, so let’s just sit back and enjoy pardoned Proud Boy Enrique Tarrio smacking the phone out of some woman’s hand and then immediately getting arrested for assault, handcuffed and carted away.
as the assaulted woman puts it,
“you don’t get to just put your hands on people. you don’t get to come here and do whatever the fuck you want. you just assaulted me, and now you’re getting arrested. good fucking job, you idiot. you pathetic piece of shit.”
she’s right, isn’t she, John Lennon?
February 27: nice try
Alexa, can grinding your jaw be a sign that you’ve hoovered way too much coke?
Cocaine jaw, also known as “coke jaw,” is a common side effect of cocaine use. It refers to the uncontrollable grinding of teeth and repetitive clenching of the jaw often observed in individuals who misuse cocaine.
oh gee.
Alexa, can putting your hand not quite to your mouth and then pretending you’re chewing on something be an effective way of masking that you’re coked to the fucking gills?
I’m going to go with no.
March 6: the flight of the Enola Homosexual
gather ’round, children, Uncle Jeff is going to read you the story of Enola, the Very Gay Airplane. it goes like this:
once upon a time, there was this ahem alleged sexual-assaulting christofascist named Piss-Drunk Pete Kegstand.
Pete was the Big Boss of the United States military. now, Pete loved the military and he loved men — but not all men. Pete only loved the manliest of men. he hated any man who wasn’t among the manliest of manly men.
now, Pete was very afraid that if his manly army of the very manliest manly men accidentally caught a glimpse of the wrong sort of word — for instance, a word like ‘gay’ — they might go a little funny in the head, and get bad ideas. and so Pete directed his military to remove all the wrong sorts of words from their files.
and that’s how the US military ended up removing photos of the Enola Gay — the plane that dropped the first atomic bomb on Japan — from its archives.
look, you imbeciles: the Enola Gay wasn’t called that because it was a boy plane that was really into other boy planes. the plane was named after Enola Gay Tibbets — the mother of Col. Paul Tibbets, its pilot.
I suppose if dear old Enola wanted a plane named after her, she should have had the decency to be named Enola Incredibly Straight Tibbets.
March 14: who would Jesus date?
christofascist pastor Joel Webbon finds himself in a bit of a sticky wicket. you see, he was hoping to sell tickets to a Christian singles event, and it seems that he’s now having to give them away for free, because … well, let’s let Joel explain.
“…completely free, and also the admission cost to the singles event. we are hoping to fill up our singles event, and finding godly Christian single women has been, well, I’ll just say, much more difficult than finding godly Christian single men.”
now comes the part where we throw back our heads in laughter.
no one could have predicted this. really weird how a bunch of unpleasant misogynistic god-botherers can’t find any women who want to attend their Incelpalooza.
hey, Pastor Joel — I’m playing gospel hits for you, on the world’s tiniest violin.
April 3: how obsequious is this?
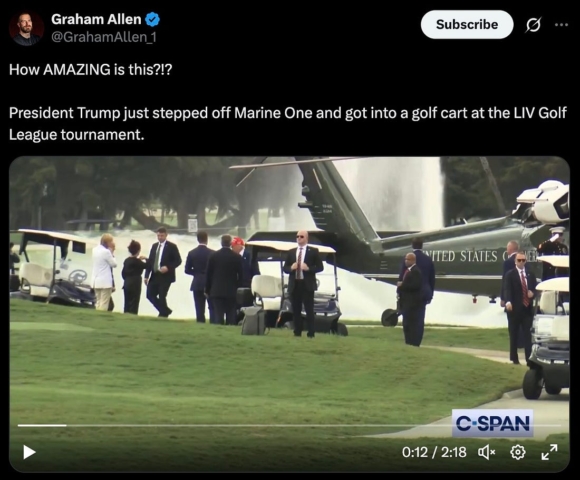
here’s what happens when you take Graham Allen, a rando MAGA podcaster, and give him a job as the Department of Defense’s ‘digital media director’:
“How AMAZING is this?!? President Trump just stepped off Marine One and got into a golf cart at the LIV Golf League tournament.”
Graham, I’ve got North Korean State TV on the phone. they’re saying to tone it down, your praise of Dear Leader is waaaaaaay too over the top.
but please, riddle me this: what the fuck is so amazing? is it that Donny didn’t waddle about with toilet paper stuck to his shoe? (October 4, 2018)
is it that a furious Slovenian rent-a-wife didn’t jump into the cart in before Donny could, and make him take the next one? (January 20, 2024)
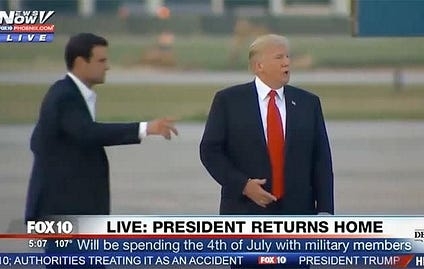
is it that Sundowning Grandpa Befuddlepants didn’t get lost on his way to the cart, and have to be guided back to it by a secret service agent? (July 6, 2017)
or is it just amazing that this dilapidated old toad —
— was able to walk twenty feet without his heart exploding?
opinion among the commenters under that not-tweet, by the way, was split between ‘yes, this is amazing’and ‘Dear Leader isn’t being fascist enough.’
April 15: oopsies!
Donny Convict’s presidential activities can be sorted into two categories: the Fucking Up Of Shit and the Standing Next To Of Athletes. Donny loves to stand next to sports dudes. anyone who wins anything, they get invited to the White House so that weak and insecure Donny can preen with them and pretend that he’s a winner, too.
on April 15, Donny must have been too busy with the Fucking Up Of Shit part of his job, because he outsourced the Standing Next To Of Athletes business to his veep.
did hilarity ensue? it sure as fuck did — because Couchfuck McGee fumbled that shit on live TV.
oh my god, JD — you had ONE JOB: picking up a championship trophy and handing it off to members of the Ohio State Buckeyes. but you couldn’t manage it without breaking the trophy in two and letting it fall from your stubby mitts.
why do they keep letting this doughy pantload out in public? is there one time when he hasn’t screwed the pooch?
hey, let’s gif that shit, for posterity’s sake — and let’s slow it way the fuck down, and wring every drop of stupid from it.
if that’s not a metaphor for Donny’s entire presidency, I don’t know what is.
April 24: go forth and multipl— never mind
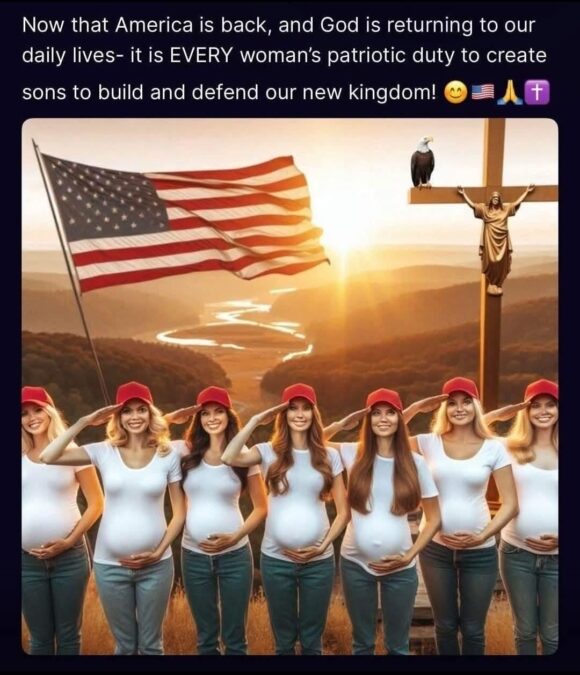
America’s christofascist dipshits have been working overtime to convince the nation’s ahem white women to boom out as many ahem white babies as possible. they’re throwing everything at the wall, just to see what sticks. let’s pay them five large to get themselves knocked up. no, wait — let’s give them medals for having six or more kids. (I’m not making this up!)
but of course, no national program to get ahem whitewomen to start fuckin’ with gusto would be complete without the distribution of ludicrous AI-generated slop.
you’ve got your godly marching orders, America’s ahem white women: get to work making sons — because apparently daughters are anathema to His Eye.
speaking of eyes, do yourself a huge favor — don’t zoom in on any of the faces.
also: what the fuck is going on behind the preggobabes? a bald eagle standing guard over a garden-gnome-sized Jesus wearing running shoes?
a brief note to whoever is responsible for this image: eagles are carrion birds. they eat dead things. is Mister Baldie here waiting for Microscopic Jesus to die, so he can chow down? is that really the message you’re intending to send to America’s fertile payload?
while we’re on the subject of horribly-rendered christofascist AI art, what prompt was input in order to come up with this abomination?
“AI, generate for me the dorkiest couple possible, and make sure the woman looks no older than twelve”?
and remember, guys: when Jesus comes to hook you up with your child bride, have your red baseball cap at the ready.
eww. these people are seriously sick.
this is going to be my closing message for the foreseeable future:
practice self-care. do what you need to do to keep sane. if that means you need to disengage with my daily posts for a while, I get it. this community of ours will still be here when you return.
to all the people who have signed on in the days since the election, welcome aboard. settle in as we all try to deal with the shitfuckery that’s ahead of us.
we are all in this together, and we are all here for each other.
OMG!
From Mock Paper Scissors:
OK, guys, this is gross and I’m sorry/not sorry to be writing about it, but it is important.
Yikes – no wonder the DOJ is scrambling to tell us not to believe what’s in the files about Trump.
www.mediaite.com/media/news/o…
— The Tennessee Holler (@thetnholler.bsky.social) December 23, 2025 at 6:50 AM
CNN has more on the Epstein-Nassar letter here, but here’s the important part:
“Dear L.N.,” the letters reads, “As you know by now, I have taken the ‘short route’ home. Good luck! We shared one thing … our love and caring for young ladies and the hope they’d reach their full potential. Our President also shares our love of young, nubile girls.” The letter makes another lewd reference to Trump’s treatment of women.
“Life is unfair,” the letter reads.
Q: is “I have taken the ‘short route’ home” some sort of euphemism saying he was killing himself?
Merde-a-Lardo itself was subpoena’ed:
Prosecutors subpoenaed Mar-a-Lago for employment records in Maxwell case
The Mar-a-Lago club was subpoenaed to produce documents in the case of United States v. Ghislaine Maxwell on Nov. 29, 2021, according to a copy of the subpoena included in the new files.
The subpoena demanded “Any and all employment records relating to [redacted].”
It is not clear who appeared on the club’s behalf.
Maxwell, a longtime associate of Epstein, was convicted of sex trafficking in 2021 and is serving a 20-year prison sentence.
“The FBI received a tip in October 2020 that appears to be from an unidentified female who said she had information about a ‘Jeffrey Epstein party’ in 2000. The person’s information is redacted in the FBI’s summary of the tip, which is included in the new files.”
“The woman alleged that someone named Ghislaine Lisa Villeneuve brought her to the party. Later, someone said that Donald Trump had invited everyone to Mar-A-Lago, according to the tipster.”
And here’s the document itself embedded as an image in this tweet.
Meanwhile, Morning Joe is carrying water for his old pal:
Scarborough: “Trump is not on Epstein’s list. There’s nothing in there really damning about Trump or Bill Clinton. So one of the great mysteries is not what Trump’s hiding, it’s why if he’s not in the files – which all the reporting says he’s not – why is he so obsessed on blocking access to them?”
— Aaron Rupar (@atrupar.com) December 22, 2025 at 7:21 AM
What The Fuck?
Sean Duffy on blue states: “What I can do is I can pull their money. That’s the leverage I do have … I guarantee you that the federal taxpayer is not going to fund their roads and bridges and their systems when they are putting illegals on the roads.”
— Aaron Rupar (@atrupar.com) December 23, 2025 at 6:27 AM
It’s almost like they know it’s all about to crash down upon and they want to get as much evil out there as possible before it happens.
And Sean, you do realize that blue states pay in the majority of Federal taxes, right?
AND EVERYONE KNOWS IT
Sunday Tiedrich
We the People are being shit on again.
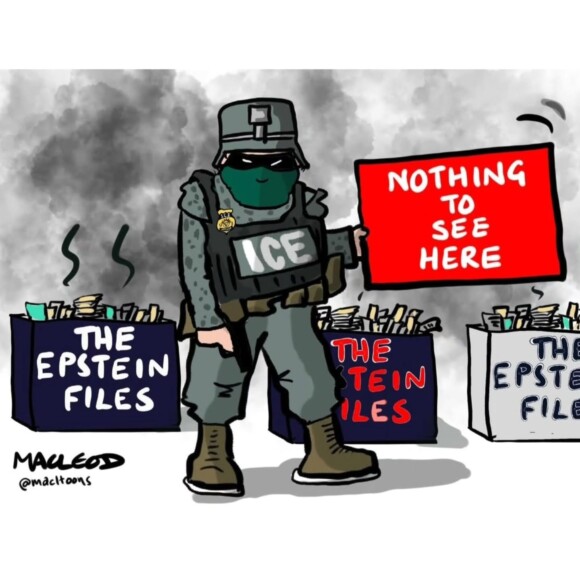
it was bad enough when Friday’s deadline came and went without Donny Convict’s corrupt Department of Justice releasing the full Epstein Files, as they were required to by law.
it was bad enough when the DOJ served us a slice of Go Fuck Yourself Pie by releasing less than one percent of the documents in their possession.
it was bad enough when hundreds upon hundreds of the documents they didrelease were completely blacked out and unreadable.
it was bad enough when it became obvious that what was released had been carefully curated to ensure there were almost zero references to Dear Leader.
but things just got a whole lot worse — because these lawless fucks are now memory-holing the shit they did release.
NEW YORK (AP) — At least 16 files disappeared from the Justice Department’s public webpage for documents related to Jeffrey Epstein — including a photograph showing President Donald Trump — less than a day after they were posted, with no explanation from the government and no notice to the public.
stuff that was already on line is now disappearing — ‘with no explanation’ — because fuck you, that’s why. what part of ‘memory hole’ do you need explained to you?
fortunately for us, the internet never forgets — so we can give you at least one explanation:
someone done fucked up and accidentally posted a photo of Dear Leader posing with bikini-clad teenagers.
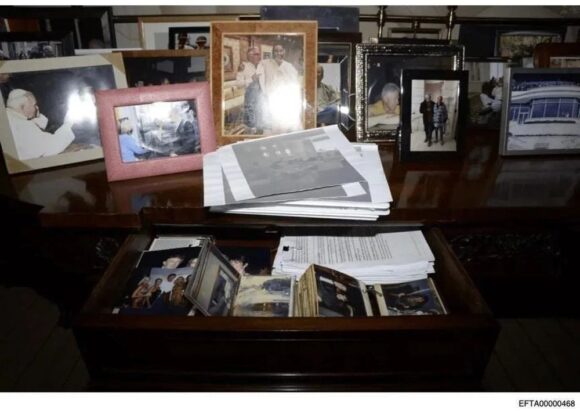
here’s ‘photo 468’ from the original collection that was posted on Friday.
let’s zoom in on the bottom left of that pic.
oh my. some bleary-eyed FBI Special Agent who’d spent a month working 20-hour days, scouring every photo for appearances of Dear Leader, missed this one.
photo 468 is now gone. if you click on the directory listing for it, you get an error message.
hey, it’s pretty weird how Jeffrey Epstein kept photos of Donny with teenage girls in his desk drawer, isn’t it? you don’t suppose Donny’s dead pedo bestie was planning on using that shit as kompromat, do you?
all these people fucking suck.
here’s another photo that got scrubbed from the DOJ web site.
why? this photo has been in the public domain for years. we’ve all seen it a hundred times.
meanwhile, Donny’s minions are doing their best to smear Bill Clinton as the real criminal in the Epstein Saga. they front-loaded the first batch of the Dead Pedo Bestie Files with as many photos of Bill as they could.
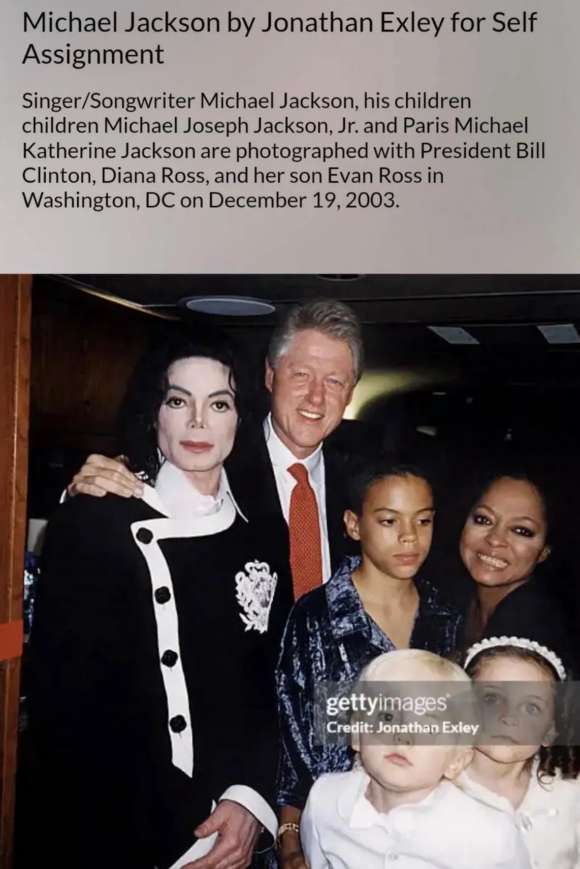
here’s White House Deputy Press Secretary Abigail Johnson, gleefully implying that Clinton and Michael Jackson were cavorting with ‘victims and/or minors.’
“Per the Epstein Files Transparency Act, DOJ was specifically instructed only to redact the faces of victims and/or minors. Here is a picture of Bill Clinton with his arm around Michael Jackson, and redacted individuals.”
for fuck’s sake, this photo doesn’t even have anything to do with Jeffrey Epstein. it’s Clinton with Michael Jackson and his children, and Diana Ross and her son, taken at a fundraiser in DC in 2003.
look, if Bill Clinton was doing sick shit with minors, nail his ass to the wall. chuck him the fuck into prison and throw away the key. I don’t think you’ll find one person on the left who would say anything different. but don’t you dare gun up fake evidence.
that’s the difference between us and them. we want justice, no matter where the chips fall. they want Dear Leader protected at all costs.
tell me, when Donny sent that birthday card to his dead pedo bestie with the poem about the ‘wonderful secrets they shared,’ do you think this is what he was talking about?
here’s another question: do words even have meanings any more? I ask, because look at the twaddle Pam Bondi posted to Elon’s Nazi Bar. she’s proud of her fuckery. she’s calling the release of heavily-redacted documents ‘transparency.’
President Trump is leading the most transparent administration in American history.
By moving to unseal these documents, we hope to give the American people more answers about that fateful day in Butler, Pennsylvania. https://t.co/v7iH9sfpiW
— Attorney General Pamela Bondi (@AGPamBondi) December 20, 2025
cool story, Pam. let’s fact-check your claim of ‘transparency.’
congratulations are in order — because Pam’s outdone George Orwell.
to ‘war is peace,’ ‘ignorance is strength,’ and ‘freedom is slavery,’ we can now add ‘censorship is transparency.’
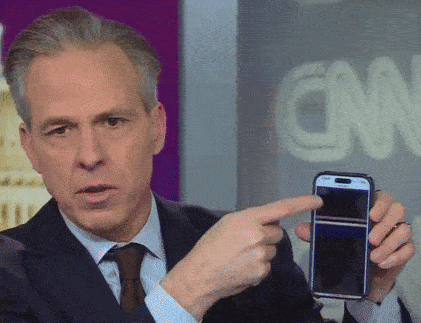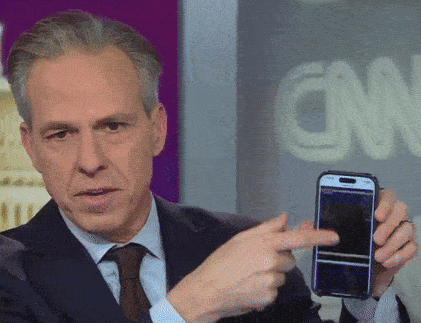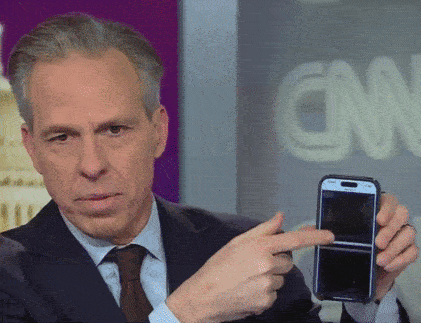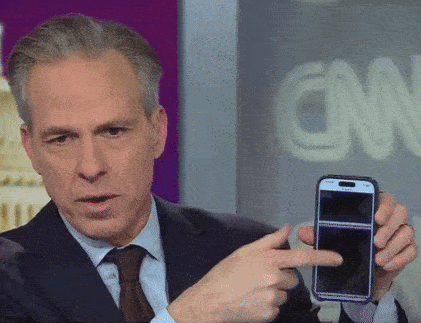
look at what else these DOJ fucksticks did: they forced Jake Tapper to commit a journalism. he hates it when he has to do that shit.
come on, people. Jake doesn’t want to be scrolling though his phone, showing you redacted files. he’s got sixteen more books to write about how Joe Biden is icky and old and smells bad and probably doesn’t even realize that he’s already dead.
“talk about blacking out, I don’t know if we can get a close-up of my phone. this is one of the documents that the Justice Department released. it’s a hundred pages. this is what it looks like. it’s all black. it’s just one hundred pages of redaction. that’s the ‘transparency’ we’re getting here.”
let’s gif that shit for posterity’s sake.
Pam Bondi’s DOJ was required by law — one that Dear Leader signed — to release everything by December 19. there were no if, and, or buts. the law didn’t say if it was too hard to get the job done in time — let’s say because there were so many references to Donny that had to be scrubbed — they get a mulligan.
they’re not supposed to crap out some unreadable tiny fraction of the files and pinky-swear to release the rest of it any day now.
oh, look at me — flapping my futile gums about what these shitstains aren’tsupposed to do.
they’re not supposed to slap Dear Leader’s name on the Kennedy Center. they’re not supposed to detain US citizens for the crime of having the wrong color skin. they’re not supposed to have the military occupy American cities. and they’re sure as fuck not supposed to murder Venezuelan sailors for the high crime of being in a boat.
unfortunately, legal accountability for suppressing the Dead Pedo Bestie Files is going to be hard to come by. sure, Congress could submit a criminal referral for obstruction of justice — but do you know who any such referral would be sent to? Pam Bondi. good luck with that.
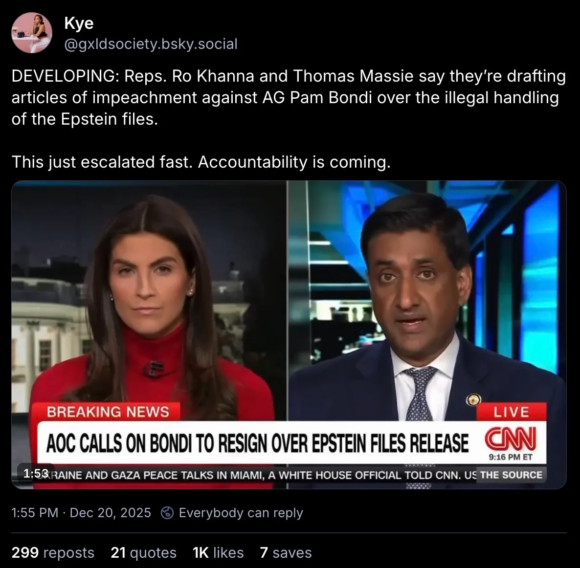
but here’s one workable option that’s already on the table: impeach the living shit out of Bondi.
“DEVELOPING: Reps. Ro Khanna and Thomas Massie say they’re drafting articles of impeachment against AG Pam Bondi over the illegal handling of the Epstein files. This just escalated fast. Accountability is coming.”
sounds like a plan.
hey Pam, you want to avoid that? fine, here’s all you have to do: release the full, unedited Epstein Files, you fucking liar.
this is going to be my closing message for the foreseeable future:
practice self-care. do what you need to do to keep sane. if that means you need to disengage with my daily posts for a while, I get it. this community of ours will still be here when you return.
to all the people who have signed on in the days since the election, welcome aboard. settle in as we all try to deal with the shitfuckery that’s ahead of us.
we are all in this together, and we are all here for each other.
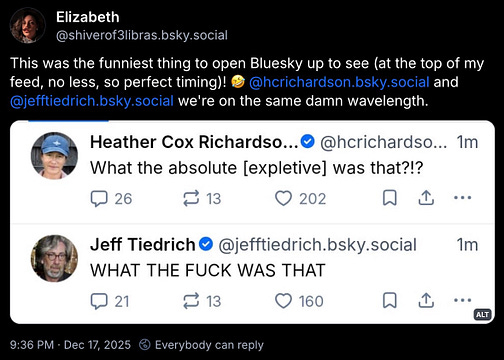
Thursday Tiedrich
what. the fuck. was that?
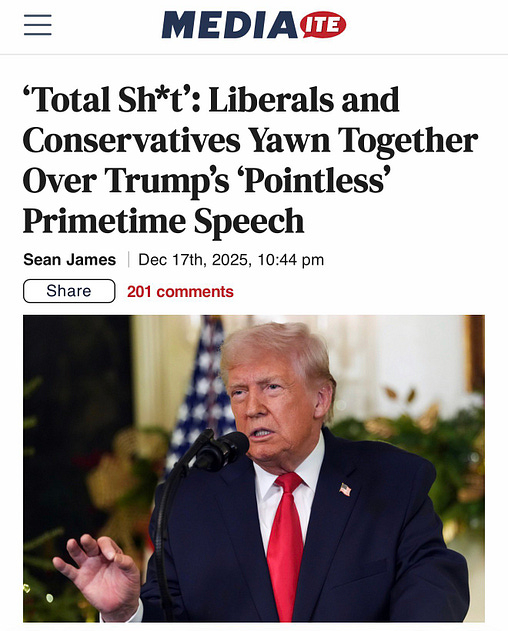
here’s what we were promised: a prime-time address to the nation, in which the President of the United States would soberly tout his achievements of the past year, and lay out his agenda for the future.
here’s what we got: some high-as-fuck shitwit, gibbering a mile a minute, gripping the podium for dear life, and barking out a non-stop barrage of obvious lies and nonsensical numbers.
“I negotiated directly with the drug companies, foreign nations, which were taking advantage of our country for many decades, to slash prices on drugs and pharmaceuticals by as much as four hundred, five hundred, and even six hundred percent. in other words, your drug costs will be plummeting downward.”
math, how does it work?
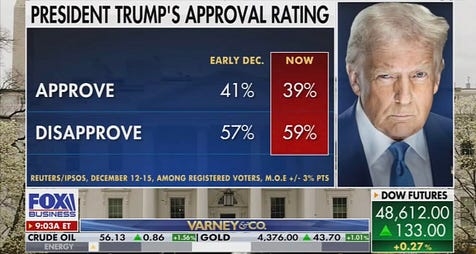
clearly, Donny and his handlers are in full panic mode. his approval numbers are in the shitter — so much so that even his own party is beginning to openly defy him. even Fox News can’t hide how toxic Donny’s become.
the magic is gone. no one but the braindeadest of his cultists believe his fever-swamp lies any more. I’m sorry, but you just can’t convince anyone who actually has to shop for groceries that prices are going down.
so what does Preznit Fuckwit do? he decides to go on TV and lie harder, and louder.
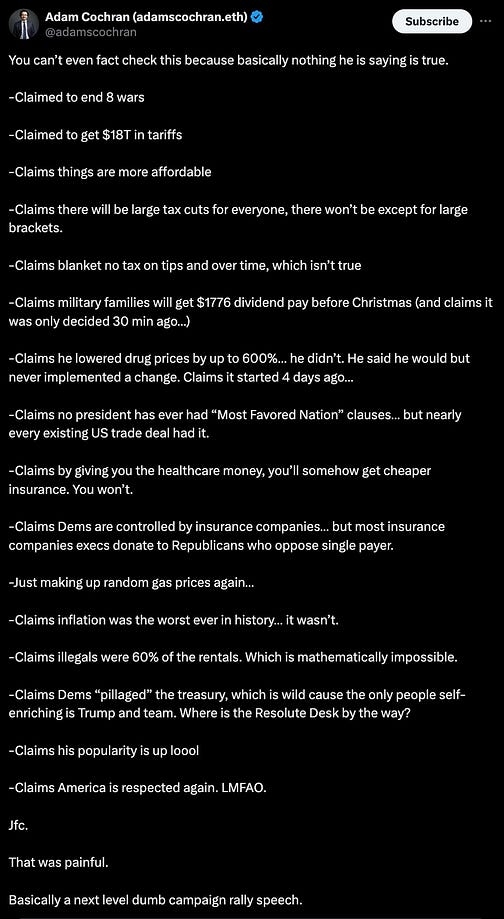
everything — and I mean everything — that came out of Donny’s rancid anus-mouth last night was a lie. he once again claimed to have ended eight wars. he hasn’t. he claimed tariffs have already brought eighteen trillion dollars into the US. they haven’t. he claimed things are already more affordable. ha fucking ha. he claimed everyone’s getting a tax cut. has he even read his own Big Stupid Bill?
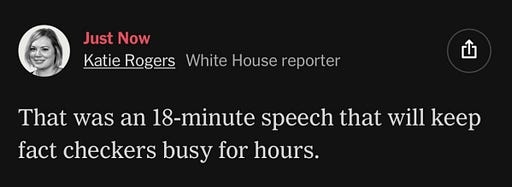
the NY Times’ White House reporter pretty much threw in the towel
investigative journalist Adam Cochran actually did a fact-check, on not-twitter. look at this encyclopedia-length screed.
the big question of the night, though, was ‘what the fuck was Donny on?’ — because he was obviously hopped up on something. he seemed ready to jump out of his skin.
clearly, Donny’s handlers didn’t want him up there looking haggard and worn out, as he pretty much always does these days — but they over-corrected.
who knows what they pumped Dear Leader full of, but it was as if the squirrels that live inside Donny’s head were having a cocaine-fueled orgy.
so there was Little Donny Motormouth, yammering away at top speed — so much so that what should have been a half-hour speech was over in just about under eighteen minutes.
when all was said and done, experts agreed: what the fuck was that?
isn’t it heartening when Republicans and Democrats can reach across the aisle to shake hands and agree that Dear Leader is crazier than a shithouse rat?
tell me, is it bad when your own party knows you’ve shit the bed?
“Why is he yelling at us?” conservative talk radio host Erick Erickson said on X.
Said right-wing blogger Matt Walsh on X: “That was perhaps the most pointless prime time presidential address ever delivered in American history.”
is it worse when your cultists think you’re stark barking bonkers?
“Trump is speaking so fast he seems panicked,” supporter Trisha Hope posted online. “I’ve never seen him like this, and I have attended 42 of his rallies.”
High energy, great delivery, grand slam, home run on making the case that the best is yet to come.
— Lindsey Graham (@LindseyGrahamSC) December 18, 2025
what can one even say? the kompromat the have on Old Linz must really be something.
who even knew that Newt Gingrich was still alive? this ancient nitwit is so far past his sell-by date that I don’t think he even knows what planet he’s on.
Gingrich: I believe President Trump showed tonight that he’s prepared to be disciplined… if I were a Democrat, tonight would leave me very unnerved. pic.twitter.com/e73vzXF5CS
— Acyn (@Acyn) December 18, 2025
“I believe President Trump showed tonight that he’s prepared to focus, to be disciplined to communicate — and if I were a Democrat, tonight would leave me very unnerved.”
it’s always fun watch Newt run away from reality as if it were a sick wife in a hospital bed, isn’t it? Democrats aren’t unnerved after watching Donny blither. Democrats are laughing their asses off.
Donny’s in desperate need of a course-correction right now, but going on TV to repeat a bunch of drug-fueled lies isn’t going to do it. everyone who isn’t being paid to pretend otherwise knows he’s full of shit, and is doing nothing to make life easier for We the People.
and things are about to get so much worse.
it was a wild fucking ride in the Holy Mike’s House of Reps yesterday.
The House on Wednesday cleared a Republican health care package, 216-211, that does not extend the expiring Affordable Care Act (ACA) subsidies.
Four moderate Republicans who had earlier Wednesday bucked GOP leaders and signed a Democratic-backed discharge petition voted in favor of the health care package. Rep. Thomas Massie was the only Republican no vote.
the healthcare bill the House passed now goes to the Senate, where it’s expected to die.
as for the discharge petition that now forces a vote on restoring the ACA subsidies, House rules allow Holy Mike to delay the actual voting until after the new year.
Johnson’s assertion came after the four Republicans broke ranks and signed onto House Democratic Leader Hakeem Jeffries’ discharge petition, giving it the 218 signatures needed to force a vote, though that is not likely to occur until January 2026 at the earliest.
which means that for millions of Americans, healthcare is going to become unaffordable after January 1st, when the ACA subsidies expire.
I can’t wait for Donny to go on TV and try to lie his way out of that.
mind you, Holy Mike could hold a vote on restoring the ACA credits right now, if he wanted to — but here’s what he’s doing instead: adjourning the House for the rest of the year, after today’s session.
what’s that thing P.J. O’Rourke used to say? oh right:
“Republicans are the party that says government doesn’t work, and then they get elected and prove it.”
here’s the other thing that happened yesterday: FBI Deputy Director Danny Bingobongo quit. officially, he’s leaving after the start of the new year — but apparently, he’s already cleaned out his desk.
Bongino had quietly told confidants he planned to formally leave his job early in the new year and would not be returning to headquarters to work this month, according to eight people briefed on his account. He later confirmed the report on X.
it seems that Danny misses his old life as a grifter and podcast bro.
“Dan did a great job,” Trump told reporters earlier, when asked about reports that Bongino, a former Secret Service agent turned podcaster, planned to resign.
“I think he wants to go back to his show,” the president said.
so, Dan’s desk at FBI headquarters is already gathering dust.
that’s certainly interesting timing, isn’t it? because the Dead Pedo Bestie Files are being released tomorrow — and I don’t know about you, but I’m as giddy with anticipation as a SecDef with a new skateboard.
this is going to be my closing message for the foreseeable future:
practice self-care. do what you need to do to keep sane. if that means you need to disengage with my daily posts for a while, I get it. this community of ours will still be here when you return.
to all the people who have signed on in the days since the election, welcome aboard. settle in as we all try to deal with the shitfuckery that’s ahead of us.
we are all in this together, and we are all here for each other.
I’m Not Holding Out Hope
Dan Quayle was an idiot who proved his idiocy time and time again. Yet Republicans insisted he was a giant, because he fit the warped mold of what they consider leadership (white, male, arrogant, rich, and full of it). It wasn’t until Quayle misspelled “potato” that his political viability came crashing down on him.
It was a nothing moment, really. Quayle didn’t even necessarily get it wrong (“potatoe” is an obsolete alternative spelling). But it was a moment that prompted everyone to see what Quayle’s critics had been saying about him from day one: he was an empty shirted buffoon.
Why am I writing about Dan Quayle of all people? Because as inconsequential as that moment was, as inconsequential as he ended up being, the “potatoe” moment still serves as a case study for something being so on the nose that it finally shattered any illusions (or delusions) that anyone was holding about him. There was really no way to defend his intellect after that; after all, the guy couldn’t even spell “potato.”
That was, of course, a comparatively innocent time. Back then we were still debating whether someone was too full of it and stupid to be President of the United States (or Vice President, as it were). We’ve since been subjected to a President of the United States who can’t spell anything, and can barely speak a coherent sentence, yet his illiteracy isn’t among the thousand most disqualifying things about him. We have a President who is a recently convicted felon, whose entire business empire has been exposed as a long running fraud with thoroughly cooked books, who was found by the courts to have sexually assaulted a woman, who tried to violently overthrow the government of the United States, who has advanced dementia and appears to be dying, who was already rejected once for being the worst President in the history of the United States… and he’s back to being President again?
The bar has been set so low over the past decade that Dan Quayle could never even get the Republican nomination because he’s far too literate – and not nearly evil enough. For some reason, for some utterly psychotic reason, Americans decided to try making the worst person in the world the President, and when that was a disastrous failure, they later decided to make him President again. There’s really nothing that could finally turn Americans against him, right?
But that’s when the on-the-nose last straw comes in. Rob Reiner, a lovely man whose life’s work has inspired millions and whose activism was marked by his dignified approach to it, was tragically murdered by his mentally unwell son. It was one of those moments that has caught everyone off guard. I loved everything about Reiner. But even if you didn’t like anything about Reiner, there’s just no way you’d root for him to go out like this, or anything like this. It’s horrifying, and except for the very fringe of internet trolls, no one was going to find any joy in this awful moment.
Even this so-called President of the United States, who openly despised Rob Reiner and everyone knew it, was surely going to sit this one out, right? This small fraction of a man, even if he was celebrating Reiner’s murder privately, surely had the sense not to say it out loud, right? And even if the Asshole-in-Chief was going to say something negative about Reiner in the wake of his murder, he’d at least… I don’t even know. You just thought that even this worthless husk of a man, whose repugnant behavior has been at its absolute worst of late, just might have stopped at the water’s edge on this one.
But no. This deranged individual occupying the Oval Office, who I’m so angry at right now that I can’t even bring myself to use his name in this article, announced that Rob Reiner got himself murdered by being too angrily opposed to – well, we’re not using his name today.
Where does one even start? Never mind that this insane man… no, you know what? I’m not even going to try to analyze it. I don’t want to know what’s going on in his rotten festering mind, and I no longer care. To hell with him. There’s nothing left to analyze, other than to observe that his dementia appears to be making his worst qualities even worse.
But this isn’t about the man whose name I can’t bring myself to type today. It’s about his supporters. It’s about how, after a decade of warning signs, flashing red lights, loud sirens, and glaringly evil thoughts expressed in exact words, this cretin finally said something that prompted many of his own most prominent supporters to loudly and publicly condemn him. It’s about how this monster finally did something that was so on-the-nose monstrous, his weary supporters could no longer hang in there and pretend it was okay – or even keep it to themselves.
There is no way to predict where this will go next. For all we know, his supporters may well fall back in line with him by the time you’re reading this article. They may even have second thoughts about what the cretin said about Rob Reiner, decide it was justified, and start parroting it themselves. It’s happened before. But yesterday felt different. It was as if they knew their toad god had finally done something so egregious that they knew they weren’t going to be able to credibly defend him on it. For one brief cogent moment on their part, they were as repulsed by this repugnant man as the rest of us have been from the start. Something finally pierced the bubble of delusion that had spent a decade pretending up was down, wrong was right, and the most vile and most destructive man on earth was somehow a classy working class hero.
We’ll see what happens now. But maybe, just maybe, something as simple as a President of the United States publicly gloating derangedly over a political adversary’s murder is finally on the nose enough to jolt his remaining supporters into acknowledging that something is very, very wrong.